CDC7-independent G1/S transition revealed by targeted protein degradation
- PMID: 35508654
- PMCID: PMC9106935
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04698-x
CDC7-independent G1/S transition revealed by targeted protein degradation
Abstract
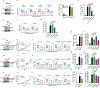
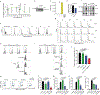
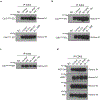
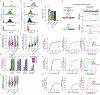
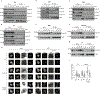
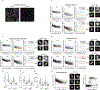
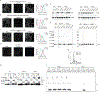
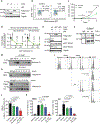
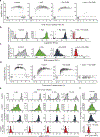
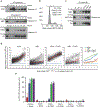
The entry of mammalian cells into the DNA synthesis phase (S phase) represents a key event in cell division1. According to current models of the cell cycle, the kinase CDC7 constitutes an essential and rate-limiting trigger of DNA replication, acting together with the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK2. Here we show that CDC7 is dispensable for cell division of many different cell types, as determined using chemical genetic systems that enable acute shutdown of CDC7 in cultured cells and in live mice. We demonstrate that another cell cycle kinase, CDK1, is also active during G1/S transition both in cycling cells and in cells exiting quiescence. We show that CDC7 and CDK1 perform functionally redundant roles during G1/S transition, and at least one of these kinases must be present to allow S-phase entry. These observations revise our understanding of cell cycle progression by demonstrating that CDK1 physiologically regulates two distinct transitions during cell division cycle, whereas CDC7 has a redundant function in DNA replication.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

