Landscape of helper and regulatory antitumour CD4+ T cells in melanoma
- PMID: 35508657
- PMCID: PMC9815755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04682-5
Landscape of helper and regulatory antitumour CD4+ T cells in melanoma
Abstract
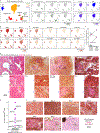
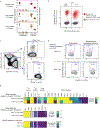
Within the tumour microenvironment, CD4+ T cells can promote or suppress antitumour responses through the recognition of antigens presented by human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II molecules1,2, but how cancers co-opt these physiologic processes to achieve immune evasion remains incompletely understood. Here we performed in-depth analysis of the phenotype and tumour specificity of CD4+ T cells infiltrating human melanoma specimens, finding that exhausted cytotoxic CD4+ T cells could be directly induced by melanoma cells through recognition of HLA class II-restricted neoantigens, and also HLA class I-restricted tumour-associated antigens. CD4+ T regulatory (TReg) cells could be indirectly elicited through presentation of tumour antigens via antigen-presenting cells. Notably, numerous tumour-reactive CD4+ TReg clones were stimulated directly by HLA class II-positive melanoma and demonstrated specificity for melanoma neoantigens. This phenomenon was observed in the presence of an extremely high tumour neoantigen load, which we confirmed to be associated with HLA class II positivity through the analysis of 116 melanoma specimens. Our data reveal the landscape of infiltrating CD4+ T cells in melanoma and point to the presentation of HLA class II-restricted neoantigens and direct engagement of immunosuppressive CD4+ TReg cells as a mechanism of immune evasion that is favoured in HLA class II-positive melanoma.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures










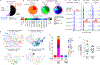

Comment in
-
Landscape of antitumor CD4+ T cells in melanoma:unraveling novel HLA class II-driven immune escape.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jan 16;8(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01307-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36646683 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 CA229092/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA079443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA101942/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA224331/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA216772/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA229261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA279391/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA090354/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA208756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA251956/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

