Single-cell N6-methyladenosine regulator patterns guide intercellular communication of tumor microenvironment that contribute to colorectal cancer progression and immunotherapy
- PMID: 35509079
- PMCID: PMC9066909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03395-7
Single-cell N6-methyladenosine regulator patterns guide intercellular communication of tumor microenvironment that contribute to colorectal cancer progression and immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation plays a critical role in key genetic events for various cancers; yet, how m6A functions within the tumor microenvironment (TME) remains to be elucidated.
Methods: A total of 65,362 single cells from single-cell RNA-seq data derived from 33 CRC tumor samples were analyzed by nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) for 23 m6A RNA methylation regulators. CRC and Immunotherapy cohorts from public repository were used to determine the prognosis and immune response of TME clusters.
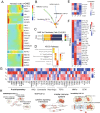
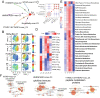
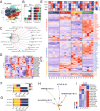
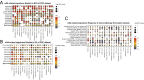
Results: The fibroblasts, macrophages, T and B cells were respectively grouped into 4 to 5 subclusters and then classified according to various biological processes and different marker genes. Furthermore, it revealed that the m6A RNA methylation regulators might be significantly related to the clinical and biological features of CRC, as well as the pseudotime trajectories of main TME cell types. Bulk-seq analysis suggested that these m6A-mediated TME cell subclusters had significant prognostic value for CRC patients and distinguished immune response for patients who underwent ICB therapy, especially for the CAFs and macrophages. Notably, CellChat analysis revealed that RNA m6A methylation-associated cell subtypes of TME cells manifested diverse and extensive interaction with tumor epithelial cells. Further analysis showed that ligand-receptor pairs, including MIF - (CD74 + CXCR4), MIF - (CD74 + CD44), MDK-NCL and LGALS9 - CD45, etc. mediated the communication between m6A associated subtypes of TME cells and tumor epithelial cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, our study firstly revealed the m6A methylation mediated intercellular communication of the tumor microenvironment in the regulation of tumor growth and antitumor immunomodulatory processes.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Immunotherapy; Prognosis; Single-cell; Tumor microenvironment; m6A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Zha X, Wang S. The role of N6-methyladenosine mRNA in the tumor microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1875:188522. - PubMed
-
- Roignant JY, Soller M. m (6)A in mRNA: An Ancient Mechanism for Fine-Tuning Gene Expression. Trends Genet. 2017;33:380–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

