Echocardiographic characteristics of PRKAG2 syndrome: a research using three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography compared with sarcomeric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 35509080
- PMCID: PMC9069802
- DOI: 10.1186/s12947-022-00284-3
Echocardiographic characteristics of PRKAG2 syndrome: a research using three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography compared with sarcomeric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: PRKAG2 syndrome is a rare disease characterized as left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), ventricular preexcitation syndrome, and sudden cardiac death. Its natural course, treatment, and prognosis were significantly different from sarcomeric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). However, it is often clinically misdiagnosed as sarcomeric HCM. PRKAG2 patients tend to experience delayed treatment. The delay may lead to adverse outcomes. This study aimed to identify the echocardiographic parameters which can differentiate PRKAG2 syndrome from sarcomeric HCM.
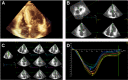
Methods: Nine PRKAG2 patients with LVH, 41 HCM patients with sarcomere gene mutations, and 202 healthy volunteers were enrolled. Clinical characteristics, conventional echocardiography, and three-dimensional images were recorded, and reviewed by an attending cardiologist. We evaluated the parameters of left ventricular strains from three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3D STE) by TomTec software. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis was used to assess clinical and echocardiographic parameters' differential diagnosis potential.
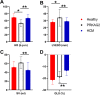
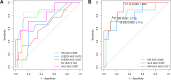
Results: The heart rate (HR) of the PRKAG2 group was significantly lower than both the healthy group (53.11 ± 10.14 vs. 69.22 ± 10.48 bpm, P < 0.001) and the sarcomeric HCM group (53.11 ± 10.14 vs. 67.23 ± 10.32 bpm, P = 0.001). The PRKAG2 group had similar interventricular septal thickness (IVS), posterior wall thickness (PWT), and maximum wall thickness (MWT) to the HCM group (P > 0.05). The absolute value of GLS in the PRKAG2 group was significantly higher than HCM patients (-18.92 ± 4.98 vs. -13.43 ± 4.30%, P = 0.004). SV calculated from EDV and ESV in PRKAG2 syndrome showed a higher value than sarcomeric HCM (61.83 ± 13.52 vs. 44.96 ± 17.53%, P = 0.020). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for HR + GLS was 0.911 (0.803 -1). For HR + GLS, the sensitivity and specificity of the best cut-off value (0.114) were 69.0% and 100%, respectively.
Conclusions: PRKAG2 patients present deteriorated LV diastolic function and preserved LV systolic function. Bradycardia and preserved GLS are useful to identify PRKAG2 syndrome from sarcomeric HCM, which may be beneficial for clinical decision-making.
Keywords: 3D STE; GLS; Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; PRKAG2 syndrome; Strain.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early changes in apical rotation in genotype positive children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations without hypertrophic changes on two-dimensional imaging.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014 Feb;27(2):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Dec 8. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014. PMID: 24325958 Clinical Trial.
-
Left ventricular dyssynchrony and 2D and 3D global longitudinal strain for differentiating physiological and pathological left ventricular hypertrophy.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017 Jun-Jul;110(6-7):403-412. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2016.11.003. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28065448
-
Role of global longitudinal strain in discriminating variant forms of left ventricular hypertrophy and predicting mortality.Anatol J Cardiol. 2021 Dec;25(12):863-871. doi: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2021.21940. Anatol J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34866580 Free PMC article.
-
The value of echocardiography in the staging of preexcitation syndrome and the assessment of left ventricular wall dyskinesia in children.Front Pediatr. 2025 Apr 25;13:1567172. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1567172. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40352602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of echocardiography in management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.J Echocardiogr. 2020 Jun;18(2):77-85. doi: 10.1007/s12574-019-00454-9. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Echocardiogr. 2020. PMID: 31858431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Echocardiographic Findings in Children of Patients Diagnosed with PRKAG2 Syndrome.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Sep 2;121(8):e20230531. doi: 10.36660/abc.20230531. eCollection 2024. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39230106 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
PRKAG2 Syndrome: Is Screening with Early Echocardiography Effective in Children with a Positive Genotype?Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024 Sep 27;121(8):e20240543. doi: 10.36660/abc.20240543. eCollection 2024. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39356949 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
-
When Paying Attention Pays Back: Missense Mutation c.1006G>A p. (Val336Ile) in PRKAG2 Gene Causing Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Conduction Abnormalities in a Caucasian Patient: Case Report and Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 23;25(17):9171. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179171. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complex Puzzle of Hypertrophic Phenotype: A Practical Approach for the Clinician.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2025 Mar;122(1):e20240529. doi: 10.36660/abc.20240529. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40197947 Free PMC article. Review. English, Portuguese.
References
-
- Gollob MH, Seger JJ, Gollob TN, Tapscott T, Gonzales O, Bachinski L, et al. Novel PRKAG2 mutation responsible for the genetic syndrome of ventricular preexcitation and conduction system disease with childhood onset and absence of cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation. 2001;104:3030–3033. doi: 10.1161/hc5001.102111. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

