Predictors of Maternal Death Among Women With Pulmonary Hypertension in China From 2012 to 2020: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
- PMID: 35509273
- PMCID: PMC9058072
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.814557
Predictors of Maternal Death Among Women With Pulmonary Hypertension in China From 2012 to 2020: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have suggested that pregnant women with pulmonary hypertension (PH) have high maternal mortality. However, indexes or factors that can predict maternal death are lacking.
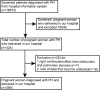
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed pregnant women with PH admitted for delivery from 2012 to 2020 and followed them for over 6 months. The patients were divided into two groups according to 10-day survival status after delivery. Predictive models and predictors for maternal death were identified using four machine learning algorithms: naïve Bayes, random forest, gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT), and support vector machine.
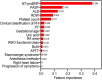
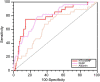
Results: A total of 299 patients were included. The most frequent PH classifications were Group 1 PH (73.9%) and Group 2 PH (23.7%). The mortality within 10 days after delivery was 9.4% and higher in Group 1 PH than in the other PH groups (11.7 vs. 2.6%, P = 0.016). We identified 17 predictors, each with a P-value < 0.05 by univariable analysis, that were associated with an increased risk of death, and the most notable were pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), platelet count, red cell distribution width, N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and albumin (all P < 0.01). Four prediction models were established using the candidate variables, and the GBDT model showed the best performance (F1-score = 66.7%, area under the curve = 0.93). Feature importance showed that the three most important predictors were NT-proBNP, PASP, and albumin.
Conclusion: Mortality remained high, particularly in Group 1 PH. Our study shows that NT-proBNP, PASP, and albumin are the most important predictors of maternal death in the GBDT model. These findings may help clinicians provide better advice regarding fertility for women with PH.
Keywords: feature importance; maternal death; predictor; pregnancy; pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Jiang, Li, Shao, Wang, Wang, Jia, Liu, An, Jing and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Machine learning-based in-hospital mortality prediction models for patients with acute coronary syndrome.Am J Emerg Med. 2022 Mar;53:127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.12.070. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Am J Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 35033770
-
[Natriuretic peptides as markers of development and prognosis of pulmonary hypertension severity in patients with chronic obstructive disease.].Klin Lab Diagn. 2018;63(6):333-337. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2018-63-6-333-337. Klin Lab Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30702222 Russian.
-
[Value of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in evaluating early septic cardiac dysfunction in neonates].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jun;32(6):711-715. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20191122-00065. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32684218 Chinese.
-
Choice of marker for assessment of RV dysfunction in acute pulmonary embolism : NT-proBNP, pulmonary artery systolic pressure, mean arterial pressure, or blood pressure index.Herz. 2017 Dec;42(8):758-765. doi: 10.1007/s00059-016-4513-6. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Herz. 2017. PMID: 27966013 English.
-
Optimized combination of circulating biomarkers as predictors of prognosis in AECOPD patients complicated with Heart Failure.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 4;18(7):1592-1599. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52405. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33746575 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A nomogram model for predicting maternal cardiovascular complications and neonatal adverse outcomes in pregnant patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2541093. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2541093. Epub 2025 Aug 4. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40758664 Free PMC article.
-
An early screening model for preeclampsia: utilizing zero-cost maternal predictors exclusively.Hypertens Res. 2024 Apr;47(4):1051-1062. doi: 10.1038/s41440-023-01573-8. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38326453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European society of cardiology (ESC) and the European respiratory society (ERS): endorsed by: association for European paediatric and congenital cardiology (AEPC), international society for heart and lung transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Respir J. (2015) 46:903–75. 10.1183/13993003.01032-2015 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

