Study on the Anticancer Activity of Prodigiosin from Variants of Serratia Marcescens QBN VTCC 910026
- PMID: 35509712
- PMCID: PMC9061010
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4053074
Study on the Anticancer Activity of Prodigiosin from Variants of Serratia Marcescens QBN VTCC 910026
Abstract
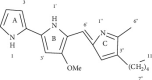
Prodigiosin (Pg), a secondary metabolism produced by numerous bacterial species, is known as anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal, immunosuppressant, antioxidant, antimalarial properties. Pg has been tested for antitumor activity in many different cancer cell lines but studies in LU-1, KB cell lines, and tumor-bearing mice are still limited. In this study, Serratia marcescens QBN VTCC 910026 strain (GenBank: KX674054.1) was mutated using Ethyl Methanesulfonate (EMS) to increase the production of Pg. One strain known as EMS 5 was capable of increasing prodigiosin biosynthetic yield by 52% when compared to the wild-type strain. Red bacterial pigmented colonies containing Pg were collected from solid media, lysed with acetone, purified with toluene: ethyl acetate at a ratio of 9: 1 (v/v), and then used to evaluate the potential anticancer activity. The purity of Pg was confirmed using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method which indicated a 98% rate. Pg chemical formula which was determined using 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy, confirmed as prodigiosin (Pg). Human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, oropharyngeal cancer KB, and particularly lung cancer LU-1 in vitro were used to test the anticancer activity of purified Pg compound. It showed a strong inhibitory ability in all the cancer cell lines. Furthermore, the isolated Pg had capable of inhibiting tumor growth, the tumor volume decreased by 36.82%, after 28 days. The results indicated that the bacterial prodigiosin from variants Serratia marcescens QBN VTCC 910026 strain is an encouraging fragment suitable for therapeutic applications.
Copyright © 2022 Sy Le Thanh Nguyen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lee J. S., Kim Y. S., Park S., et al. Exceptional production of both prodigiosin and cycloprodigiosin as major metabolic constituents by a novel marine bacterium, Zooshikella rubidus S1-1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology . 2011;77(14):4967–4973. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01986-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

