Cognitive interventions in mature and older adults, benefits for psychological well-being and quality of life: a systematic review study
- PMID: 35509795
- PMCID: PMC9018088
- DOI: 10.1590/1980-57642021dn15-040002
Cognitive interventions in mature and older adults, benefits for psychological well-being and quality of life: a systematic review study
Abstract
Few recently published studies investigating the benefits of educational and cognitive interventions on quality of life (QoL), psychological well-being, and depressive symptoms are available.
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of educational and cognitive interventions on psychological well-being, QoL, and mood in mature and older adults without dementia and/or with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
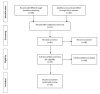
Methods: The systematic review took place from September to October 2020 and the following databases were used to select the studies: SciELO, LILACS, PubMed, and Medline. The search terms used were idos* AND "treino cognitivo" AND "bem-estar psicológico" AND "qualidade de vida" and their corresponding translations in English and Spanish.
Results: Of the 241 articles retrieved, 26 primary studies were included in the review. Of these, 18 showed improvement in QoL, psychological well-being, or cognition.
Conclusions: The studies reported beneficial effects of educational and cognitive interventions for QoL, psychological well-being, and depressive symptoms of mature and older adults without dementia or depression.
Nos últimos anos, foram encontrados poucos estudos relatando os benefícios das intervenções cognitivas e educativas à qualidade de vida, ao bem-estar psicológico e contra os sintomas depressivos.
Objetivo: Investigar os impactos de intervenções educativas e cognitivas nas variáveis de bem-estar psicológico, qualidade de vida e humor de adultos maduros e idosos sem demência e/ou com comprometimento cognitivo leve.
Métodos: A pesquisa de revisão sistemática ocorreu entre setembro e outubro de 2020 e, para a seleção dos estudos, foram utilizadas as bases de dados: Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO), Literatura Latino-Americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde (Lilacs), PubMed e Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE). Foram selecionados os seguintes termos para a busca: “idos*” AND “treino cognitivo” AND “bem-estar psicológico” AND “qualidade de vida” e seus correspondentes em inglês e espanhol.
Resultados: De 241 artigos contendo as palavras-chave, 26 estudos primários foram selecionados para esta revisão. Deles, 18 demonstraram melhora significativa na qualidade de vida, no bem-estar psicológico ou na cognição.
Conclusões: Os estudos analisados evidenciaram efeitos positivos das intervenções educacionais e cognitivas para a qualidade de vida, para o bem-estar psicológico e contra os sintomas depressivos de idosos e adultos maduros sem demência e depressão.
Keywords: aging; cognitive aging; depressive symptoms; educational activities; quality of life; social neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oliveira AS, Silva VC, Confort MF. Benefícios da estimulação cognitiva aplicada ao envelhecimento. Rev Episteme Transversalis. 2017;8(2):16–31.
-
- Organização Mundial de Saúde Relatório mundial de envelhecimento e saúde. 2015. [2020 Oct, 22]. Available from: https://sbgg.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/OMS-ENVELHECIMENTO-2015-p... .
-
- Karsch UM. In: Envelhecimento com dependência: cuidados e cuidadores de idosos. Salimene AC, Oliveira B, Hayar MA, editors. São Paulo: Portal Edições; 2019. Envelhecimento com dependência e cuidadores - introduzindo a temática; p. 12.
-
- Oliveira DS de, Lima MP, Ratto CG, Rossi T, Baptista RR, Irigaray TQ. Avaliação de bem-estar psicológico e sintomas depressivos em idosos saudáveis. Estud Pesqui Psicol. 2020;20(1):187–204. doi: 10.12957/epp.2020.50796. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources