Low cost, non-invasive, and continuous vital signs monitoring device for pregnant women in low resource settings (Lvital device)
- PMID: 35509911
- PMCID: PMC9058728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ohx.2022.e00276
Low cost, non-invasive, and continuous vital signs monitoring device for pregnant women in low resource settings (Lvital device)
Abstract
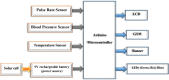
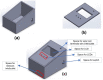
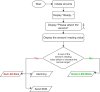
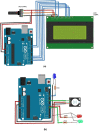
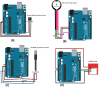
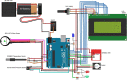
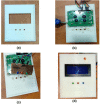
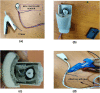
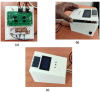
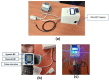
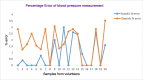
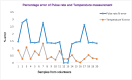
Around 800 women die each day from complications of pregnancy and childbirth in the world. Vital Signs monitoring (such as blood pressure, pulse rate, and temperature) are among fundamental parameters of ensuring the health and safety of women and newborns during pregnancy, labor, and childbirth. Approximately, 10% of women experience hypertension (greater than140/90) during pregnancy. High blood pressure during pregnancy can cause extra stress on the heart and kidneys and can increase the risk of heart disease. Therefore, early recognition of abnormal vital signs, which are induced due to pregnancy can allow for timely identification of clinical deterioration. Currently used technologies are expensive and complex design with implementation challenges in low-resource settings where maternal morbidity and mortality is higher. Thus, considering the above need, here a hardware device has been designed and developed, which is a low cost, and portable for pregnant women's vital signs (with cuff-less blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature) monitoring device. The developed device would have a remarkable benefit of monitoring the maternal vital signs especially for those in low resource settings, where there is a high paucity of vital signs monitoring devices.
Keywords: 3D print; Blood Pressure; Cuffless; Pulse rate; Temperature; Vital signs.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Comprehensive pregnancy monitoring with a network of wireless, soft, and flexible sensors in high- and low-resource health settings.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 18;118(20):e2100466118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2100466118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33972445 Free PMC article.
-
The CRADLE vital signs alert: qualitative evaluation of a novel device designed for use in pregnancy by healthcare workers in low-resource settings.Reprod Health. 2018 Jan 5;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12978-017-0450-y. Reprod Health. 2018. PMID: 29304812 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a novel Vital Signs Alert device for use in pregnancy in low-resource settings.BMJ Innov. 2018 Oct;4(4):192-198. doi: 10.1136/bmjinnov-2017-000235. Epub 2018 Sep 19. BMJ Innov. 2018. PMID: 30319784 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in vital signs measurement for the detection of hypertension and shock in pregnancy.Reprod Health. 2018 Jun 22;15(Suppl 1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12978-018-0533-4. Reprod Health. 2018. PMID: 29945641 Free PMC article.
-
Universal access to essential vital signs monitoring.Anesth Analg. 2013 Oct;117(4):883-890. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a1f22f. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 24023026 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a New Smartphone Powered Low-cost Pulse Oximeter Device.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2022 Jul;32(4):841-848. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v32i4.22. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 35950062 Free PMC article.
-
Parental perceptions of a wearable vital signs monitor for observation of newborns: in-depth interviews in three tertiary hospitals, Southwest Nigeria.Front Digit Health. 2025 Jul 28;7:1597651. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1597651. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40791998 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Low-Cost and Portable Pulse Oximeter Device with Improved Accuracy and Accessibility.Med Devices (Auckl). 2022 May 5;15:121-129. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S366053. eCollection 2022. Med Devices (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35547098 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Insights: Enhanced Vision Transformers for the Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;16(7):1441. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071441. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611117 Free PMC article.
-
Vision-Transformer-Based Transfer Learning for Mammogram Classification.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;13(2):178. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13020178. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- B. Wassihun, B. Negese, H. Bedada, S. Bekele, A. Bante, T. Yeheyis, A. Abebe, D. uli, M. Mohammed, S. Gashawbez, E. Hussen, Knowledge of obstetric danger signs and associated factors: a study among mothers in Shashamane town, Oromia region, Ethiopia, Reprod. Health, 17(4) (2020). 10.1186/s12978-020-0853-z - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sandsæter H.L., Horn J., Rich-Edwards J.W., Haugdahl H.S. Preeclampsia, gestational diabetes and later risk of cardiovascular disease: Women’s experiences and motivation for lifestyle changes explored in focus group interviews. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19:448. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2591-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

