Investigation of HPLF-111624 in Modified Experimental Models of Ulcerative Proctitis and Anal Fissure in Rats
- PMID: 35509969
- PMCID: PMC9058020
- DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S345599
Investigation of HPLF-111624 in Modified Experimental Models of Ulcerative Proctitis and Anal Fissure in Rats
Abstract
Background: Although ulcerative proctitis (UP) and anal fissure (AF) are common anorectal diseases, there are no appropriate experimental models to screen the drugs intended for these conditions. In this context, existing experimental models mimicking these diseases were modified and the polyherbal formulation, HPLF-111624 was evaluated in these models.
Objective: To establish animal model for UP and AF and to evaluate polyherbal formulation, HPLF-111624 in these disease models.
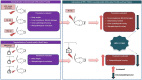
Methods: An experimental model of UP was selected based on the modification of the ulcerative colitis model using different concentrations of acetic acid. The concentration used for induction were 2.5%, 5% and 10% v/v and different weights used to induce AF were 25 g, 50 g and 100 g, which were selected based on the severity of inflammation, fecal score, gross pathology, and histopathological evaluation. Furthermore, these animal models were used to evaluate the efficacy of HPLF-111624, a polyherbal formulation known to be beneficial in anal diseases.
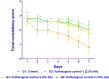
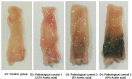
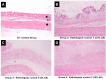
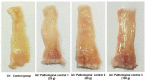
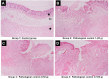
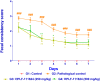
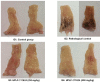
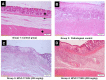
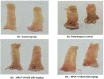
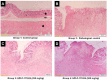
Results: Acetic acid at 5% produced typical pathological changes that resembled UP, with a significant increase in the fecal score, gross lesion, and histopathological changes. Similarly, among the three weights, physical injury with a 100 g weight produced significant changes in the histopathological score in the model of AF. Intervention with HPLF-111624 at doses of 250 and 500 mg/kg b.wt., showed a reduction in the inflammatory cytokines and a significant improvement in the histopathological findings in both the conditions.
Conclusion: The results showed that the modified experimental models for UP and AF resemble the human pathological conditions and are simple, versatile and may be used for screening drugs intended for these conditions. Intervention with HPLF-111624 was found to be effective in improving the pathological state of UP and AF.
Keywords: anal fissure; anorectal disorders; histopathological evaluation; inflammation; polyherbal formulation; ulcerative proctitis.
© 2022 Onkaramurthy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are employees of Himalaya Wellness Company, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Different Doses of Herbal Cake-partitioned Moxibustion on Histopathological Changes of Colon Tissue in Ulcerative Colitis Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Feb 25;43(2):68-74. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170843. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 29516692 Chinese.
-
Effect of polyherbal formulation on experimental models of inflammatory bowel diseases.J Ethnopharmacol. 2004 Feb;90(2-3):195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.09.042. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15013181
-
Gisekia pharnaceoides Restores Colonic Mucosal Homeostasis by Regulating Antioxidant Enzyme System and Cytokines Signaling in Ulcerative Colitis Mice Model.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022;22(1):133-142. doi: 10.2174/1871530321666211109151737. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34751126
-
[Fistula, fissure, abscess].Chirurg. 1996 Mar;67(3):222-8. Chirurg. 1996. PMID: 8681694 Review. German.
-
The treatment of refractory ulcerative colitis.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018 Feb-Apr;32-33:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 18. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30060939 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

