Prednisone plus IVIg compared with prednisone or IVIg for immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy: a national retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 35510211
- PMCID: PMC9058461
- DOI: 10.1177/20406207221095226
Prednisone plus IVIg compared with prednisone or IVIg for immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy: a national retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The responses of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) or corticosteroids as the initial treatment on pregnancy with ITP were unsatisfactory. This study aimed to assess the safety and effectiveness of prednisone plus IVIg versus prednisone or IVIg in pregnant patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
Methods: Between 1 January 2010 and 31 December 2020, 970 pregnancies diagnosed with ITP at 19 collaborative centers in China were reviewed in this observational study. A total of 513 pregnancies (52.89%) received no intervention. Concerning the remaining pregnancies, 151 (33.04%) pregnancies received an initial treatment of prednisone plus IVIg, 105 (22.98%) pregnancies received IVIg alone, and 172 (37.64%) pregnancies only received prednisone.
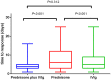
Results: Regarding the maternal response to the initial treatment, no differences were found among the three treatment groups (41.1% for prednisone plus IVIg, 33.1% for prednisone, and 38.1% for IVIg). However, a significant difference was observed in the time to response between the prednisone plus IVIg group (4.39 ± 2.54 days) and prednisone group (7.29 ± 5.01 days; p < 0.001), and between the IVIg group (6.71 ± 4.85 days) and prednisone group (p < 0.001). The median prednisone duration in the monotherapy group was 27 days (range, 8-195 days), whereas that in the combination group was 14 days (range, 6-85 days). No significant differences were found among these three treatment groups in neonatal outcomes, particularly concerning the neonatal platelet counts. The time to response in the combination treatment group was shorter than prednisone monotherapy. The duration of prednisone application in combination group was shorter than prednisone monotherapy. The combined therapy showed a lower predelivery platelet transfusion rate than IVIg alone.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that prednisone plus IVIg may represent a potential combination therapy for pregnant patients with ITP.
Keywords: immune thrombocytopenia; intravenous immunoglobulin; prednisone; pregnant.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety Analysis of Combination Therapy Consisting of Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Corticosteroids versus Respective Monotherapies in the Treatment of Relapsed ITP in Adults.Glob Med Genet. 2023 May 23;10(2):87-96. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1769087. eCollection 2023 Jun. Glob Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37228869 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of glucocorticoid compared with immunoglobulin therapy of severe immune thrombocytopenia during pregnancy: Response rate and complication.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018 Oct;80(4):e13000. doi: 10.1111/aji.13000. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30010227
-
Corticosteroids compared with intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy.Blood. 2016 Sep 8;128(10):1329-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-04-710285. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27402971
-
Immune thrombocytopenia and COVID-19: Case report and review of literature.Lupus. 2021 Aug;30(9):1515-1521. doi: 10.1177/09612033211021161. Epub 2021 May 30. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 34053365 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Anti-D Immunoglobulins versus Intravenous Immunoglobulins for Immune Thrombocytopenia in Children: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Pediatr. 2019 Jan;204:225-233.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.07.065. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30314658
Cited by
-
Recombinant human thrombopoietin therapy for primary immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy: a retrospective comparative cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Nov 27;23(1):820. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06134-y. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 38012579 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety Analysis of Combination Therapy Consisting of Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Corticosteroids versus Respective Monotherapies in the Treatment of Relapsed ITP in Adults.Glob Med Genet. 2023 May 23;10(2):87-96. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1769087. eCollection 2023 Jun. Glob Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37228869 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia During Pregnancy With Management Strategies and Considerations: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 21;16(8):e67449. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67449. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39314573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Predictive Model for Treatment Effectiveness in Severe Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia during Pregnancy: A Retrospective Study in a Tertiary Critical Maternity Referral Center.Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025;90(2):153-164. doi: 10.1159/000541721. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2025. PMID: 39369706 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia During Pregnancy: Management Strategies and Considerations: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 20;16(8):e67284. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67284. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39301384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gill KK, Kelton JG. Management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in pregnancy. Semin Hematol 2000; 37: 275–289. - PubMed
-
- Sainio S, Kekomaki R, Riikonen S, et al.. Maternal thrombocytopenia at term: a population-based study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000; 79: 744–749. - PubMed
-
- Cines DB, Blanchette VS. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 995–1008. - PubMed
-
- Eslick R, McLintock C. Managing ITP and thrombocytopenia in pregnancy. Platelets 2020; 31: 300–306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

