Quercetin ameliorates Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 35510228
- PMCID: PMC9052324
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfac006
Quercetin ameliorates Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
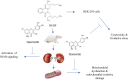
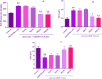
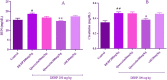
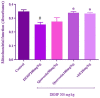
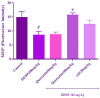
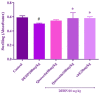
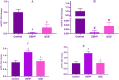
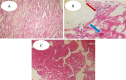
This study aimed to evaluate the possible protective effects of quercetin, a natural flavonoid, against nephrotoxicity induced by Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in kidney tissue of rats and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cell line. The HEK-293 cells were treated with different concentrations of quercetin 24 h before treatment with monoethylhexyl phthalate (MEHP). Male rats were treated with 200-mg/kg DEHP, 200-mg/kg DEHP plus quercetin (50 and 100 mg/kg), and 200-mg/kg DEHP plus vitamin E (20 mg/kg) for 45 days by gavage. Quercetin treatment reduced cytotoxicity and oxidative damage inducing by MEHP in HEK-293 cells. The in vivo findings showed that 100-mg/kg quercetin significantly suppressed DEHP-induced kidney damage. For exploring the involved mechanisms, the expressions of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) genes were determined via real-time Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. High dose of quercetin significantly decreased the gene expressions of NF-κB and TNFα, whereas the alternations of Nrf2 and HO-1 gene expressions were not significant in quercetin groups in compared with DEHP group. These findings suggested that the suppression of DEHP-induced nephrotoxicity via quercetin is correlated, at least in part, with its potential to regulate NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate; HEK293 cell line; mitochondria; nephrotoxicity; nuclear factor kappa B; quercetin.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dimethyl Fumarate Attenuates Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2023 Feb;46(1):453-467. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01746-6. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36195817
-
The implication of mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial oxidative damage in di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induced nephrotoxicity in both in vivo and in vitro models.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2020 Jul;30(6):427-437. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2020.1758980. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2020. PMID: 32312132
-
Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induces cytotoxicity in HEK-293 cell line, implication of the Nrf-2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway.Environ Toxicol. 2019 Sep;34(9):1034-1042. doi: 10.1002/tox.22774. Epub 2019 May 21. Environ Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31112013
-
Mangiferin mitigates di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular injury in rats by modulating oxidative stress-mediated signals, inflammatory cascades, apoptotic pathways, and steroidogenesis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Oct 30;711:108982. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2021.108982. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34400143
-
The impact of Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Mono(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate in placental development, function, and pathophysiology.Environ Int. 2021 Jan;146:106228. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106228. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Environ Int. 2021. PMID: 33157377 Review.
Cited by
-
Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate mediates oxidative stress and activates p38MAPK/NF-kB to exacerbate diabetes-induced kidney injury in vitro and in vivo models.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Apr 1;12(2):332-343. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad022. eCollection 2023 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37125328 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin prevents rats from type 1 diabetic liver damage by inhibiting TGF-ꞵ/apelin gene expression.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024 Sep 17;7:100201. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2024.100201. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39351284 Free PMC article.
-
Morin hydrate ameliorates Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) induced hepatotoxicity in a mouse model via TNF-α and NF-κβ signaling.3 Biotech. 2024 Jul;14(7):181. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04012-8. Epub 2024 Jun 18. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38911474 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane substantially impedes testicular ferroptosis in adult rats exposed to di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate through activation of NRF-2/SLC7A11/GPX-4 trajectory.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;398(3):3163-3175. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03440-w. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39352535 Free PMC article.
-
The ameliorative effects of quercetin and curcumin against subacute nephrotoxicity of fipronil induced in Wistar rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 May 22;12(3):493-502. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad034. eCollection 2023 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37397921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aydemir D, Karabulut G, Şimşek G, Gok M, Barlas N, and Ulusu N. Impact of the Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate administration on trace element and mineral levels in relation of kidney and liver damage in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018:186(2):474–488. - PubMed
-
- Dong J, Ma Y, Leng K, Wei L, Wang Y, Su C, Liu M, Chen J. Associations of urinary di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate metabolites with the residential characteristics of pregnant women. Sci Total Environ. 2020:707(10):135671. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Zhang W, Rui B, Yang S, Xu W, Wei W. Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exacerbates non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats and its potential mechanisms. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016:42(2):38–44. - PubMed
-
- Kamijo Y, Hora K, Nakajima T, Kono K, Takahashi K, Ito Y, Higuchi M, Kiyosawa K, Shigematsu H, Gonzalez F, Aoyama T. Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor α protects against glomerulonephritis induced by long-term exposure to the plasticizer Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007:18(1):176–188. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

