PGI score: prospective validation and correlation with SOFA, SAPS-II, and APACHE-II scores for predicting outcomes in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning
- PMID: 35510238
- PMCID: PMC9052320
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfac015
PGI score: prospective validation and correlation with SOFA, SAPS-II, and APACHE-II scores for predicting outcomes in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning
Abstract
Introduction: We recently derived a simplified 3-point PGI score (representing blood pH < 7.25, Glasgow coma scale [GCS] score < 13, and impaired systolic blood pressure [SBP] < 90 mm Hg), which accurately predicted in-hospital case fatality ratio (CFR) in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning. The present study aimed to validate the PGI score and compare it with Acute Physiologic Assessment and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score (SOFA), and Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS) II scores.
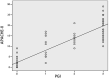
Patients and methods: We performed a prospective cohort study in adult patients with aluminum phosphide ingestion admitted in PGIMER, Chandigarh (India), from April 2013 to August 2014. A univariant analysis detected the association of various baseline variables with CFR. Correlation of the PGI score with SOFA, SAPS-II, and APACHE-II scores was performed using Spearman's correlation (rs , range -1 to +1) and scatter plots.
Results: Seventy-six patients were enrolled (mean age, 28.3 years; 41 males). CFR was 60.5%. PGI score variables-pH, GCS, and impaired SBP predicted CFR (P-value <0.001). Among patients with a total PGI score of 3 or 2, 100% died, compared with 50% in score 1 and 10.7% in score 0. Baseline PGI, SOFA, SAPS-II, and APACHE-II scores predicted CFR (P-value <0.001). There was a positive correlation between the PGI score and SOFA score (rs , 0.855), SAPS-II score (rs , 0.861), and APACHE-II score (rs , 0.883). The P-value for all rs values was <0.001.
Conclusion: The PGI score is a validated toxidrome-specific and simplified risk-stratification tool. Validation in other populations is warranted to confirm its routine use.
Keywords: APACHE-II; PGI; SAPS-II; SOFA; aluminum phosphide; case fatality ratio; predicting tool; prognosis; scoring system.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of SOFA-based models for predicting mortality in the ICU: A systematic review.Crit Care. 2008;12(6):R161. doi: 10.1186/cc7160. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Crit Care. 2008. PMID: 19091120 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
A Retrospective Analysis of the Predictive Role of RDW, MPV, and MPV/PLT Values in 28-Day Mortality of Geriatric Sepsis Patients: Associations with APACHE II and SAPS II Scores.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jul 22;61(8):1318. doi: 10.3390/medicina61081318. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40870363 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of norepinephrine equivalence score on the 28-day death risk in patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Apr;37(4):331-336. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240413-00341. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40814704 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 performance: a systematic review of external validation studies.Crit Care. 2014 Jun 6;18(3):R117. doi: 10.1186/cc13911. Crit Care. 2014. PMID: 24906651 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of poison-related factors and consumption patterns in acute aluminum phosphide poisoning.Turk J Emerg Med. 2023 Jan 2;23(2):88-95. doi: 10.4103/tjem.tjem_253_22. eCollection 2023 Apr-Jun. Turk J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37169035 Free PMC article.
-
Shock and modified shock indices in predicting poisoning severity and outcomes in acute aluminum phosphide poisoned patients.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Dec 30;13(1):tfad124. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad124. eCollection 2024 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 38173544 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of different scores for mortality prediction of acutely poisoned patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jun 21;14(3):tfaf080. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf080. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40585421
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as mortality predictors in acute Aluminum phosphide (grain pills) poisoning: clinical insights and risk assessment.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Dec 13;13(6):tfae212. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae212. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39677490
-
Role of serum glucose/potassium ratio in assessing poisoning severity and adverse outcomes in patients with acute aluminum phosphide poisoning.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Feb 4;14:101947. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101947. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40026479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anbalagan LC, Arora N, Pannu AK. Management of acute aluminum phosphide poisoning: has anything changed? Drug Metab Lett. 2021:14(2):106–116. - PubMed
-
- Shadnia S, Sasanian G, Allami P, Hosseini A, Ranjbar A, Amini-Shirazi N, Abdollahi M. A retrospective 7-years study of aluminum phosphide poisoning in Tehran: opportunities for prevention. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2009:28(4):209–213. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous