Bioinformatic Analyzes of the Association Between Upregulated Expression of JUN Gene via APOBEC-Induced FLG Gene Mutation and Prognosis of Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 35510248
- PMCID: PMC9058067
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.815450
Bioinformatic Analyzes of the Association Between Upregulated Expression of JUN Gene via APOBEC-Induced FLG Gene Mutation and Prognosis of Cervical Cancer
Abstract
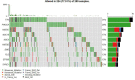
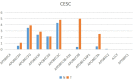
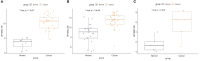
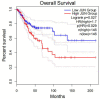
Globally, cervical cancer (CC) is the most common malignant tumor of the female reproductive system and its incidence is only second after breast cancer. Although screening and advanced treatment strategies have improved the rates of survival, some patients with CC still die due to metastasis and drug resistance. It is considered that cancer is driven by somatic mutations, such as single nucleotide, small insertions/deletions, copy number, and structural variations, as well as epigenetic changes. Previous studies have shown that cervical intraepithelial neoplasia is associated with copy number variants (CNVs) and/or mutations in cancer-related genes. Further, CC is also related to genetic mutations. The present study analyzed the data on somatic mutations of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC) in the Cancer Genome Atlas database. It was evident that the Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme-catalyzed polypeptide-like (APOBEC)-related mutation of the FLG gene can upregulate the expression of the JUN gene and ultimately lead to poor prognosis for patients with CC. Therefore, the findings of the current study provide a new direction for future treatment of CC.
Keywords: APOBEC; FLG; JUN; cervical cancer; mutation.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhao, Liu, Zhou, Wang, Fang and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

