Thapsigargin blocks electromagnetic field-elicited intracellular Ca2+ increase in HEK 293 cells
- PMID: 35510320
- PMCID: PMC9069166
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15189
Thapsigargin blocks electromagnetic field-elicited intracellular Ca2+ increase in HEK 293 cells
Abstract
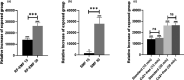
Biological effects of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) have previously been identified for cellular proliferation and changes in expression and conduction of diverse types of ion channels. The major effect elicited by EMFs seems to be directed toward Ca2+ homeostasis. This is particularly remarkable since Ca2+ acts as a central modulator in various signaling pathways, including, but not limited to, cell differentiation and survival. Despite this, the mechanisms underlying this modulation have yet to be unraveled. Here, we assessed the effect of EMFs on intracellular [Ca2+ ], by exposing HEK 293 cells to both radio-frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMFs) and static magnetic fields (SMFs). We detected a constant and significant increase in [Ca2+ ] subsequent to exposure to both types of fields. Strikingly, the increase was nulled by administration of 10 μM Thapsigargin, a blocker of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ -ATPases (SERCAs), indicating the involvement of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in EMF-related modulation of Ca2+ homeostasis.
Keywords: calcium; electromagnetic fields; endoplasmic reticulum; intracellular dynamics.
© 2022 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


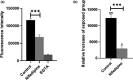
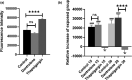
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+-ATPase by thapsigargin analogs induces cell death via ER Ca2+ depletion and the unfolded protein response.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 1;292(48):19656-19673. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796920. Epub 2017 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972171 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical effects of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) activator gingerol on NG115-401L neuronal cells: failure to augment ER Ca(2+) uptake and protect against ER stress-induced cell death.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 5;762:165-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.05.055. Epub 2015 May 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26033206
-
Changes in intracellular Ca2+ and pH in response to thapsigargin in human glioblastoma cells and normal astrocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):C361-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00280.2004. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15800052
-
Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum-Ca-ATPase by glycolysis in eukaryotic cells.Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996;22(5-6):318-35. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996. PMID: 8933503 Review.
-
A tool coming of age: thapsigargin as an inhibitor of sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPases.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998 Apr;19(4):131-5. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(98)01184-5. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9612087 Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to Low-Frequency Radiation Changes the Expression of Nestin, VEGF, BCRP and Apoptosis Markers During Glioma Treatment Strategy: An In Vitro Study.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(1):55-67. doi: 10.2174/0118744710258350230921065159. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 38817005
-
Gathering Evidence to Leverage Musculoskeletal Magnetic Stimulation Towards Clinical Applicability.Small Sci. 2024 Feb 26;4(5):2300303. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202300303. eCollection 2024 May. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40213569 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of thapsigargin as an antiviral agent against transmissible gastroenteritis virus.Vet Res. 2024 Aug 2;55(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01359-x. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39095890 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channels as molecular targets of glioblastoma electrotherapy.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 17;17:1133984. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1133984. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37006466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aoyama, M. , Yamada, A. , Wang, J. , Ohya, S. , Furuzono, S. , Goto, T. , Hotta, S. , Ito, Y. , Matsubara, T. , Shimokata, K. , Chen, S. R. W. , Imaizumi, Y. , & Nakayama, S. (2004). Requirement of ryanodine receptors for pacemaker Ca2+ activity in ICC and HEK293 cells. Journal of Cell Science, 117, 2813–2825. 10.1242/jcs.01136 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Balassa, T. , Varró, P. , Elek, S. , Drozdovszky, O. , Szemerszky, R. , Világi, I. , & Bárdos, G. (2013). Changes in synaptic efficacy in rat brain slices following extremely low‐frequency magnetic field exposure at embryonic and early postnatal age. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 31, 724–730. 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.08.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

