Mechanical Needling With Sterile Water Versus Lidocaine Injection for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
- PMID: 35510334
- PMCID: PMC10676179
- DOI: 10.1177/21925682221094533
Mechanical Needling With Sterile Water Versus Lidocaine Injection for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Abstract
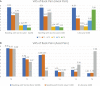
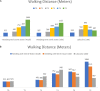
Study Design: This was a retrospective observational study that assessed the clinical outcome of ageing patients who received ultrasound-guided (USG) mechanical needling with sterile water injection. In addition, the clinical outcome of age-and gender matched patients randomly selected from patients who received needling with sterile water was compared to the patients injected with lidocaine in a 1:1 ratio.Objective: This present study aimed to explore the clinical effects of USG mechanical needling with sterile water injection for lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS).Methods: The data was extracted from the medical records of ageing patients with LSS who received USG injection at the lumbosacral spine by the first author. Low back pain or axial pain, and leg pain or radicular pain were assessed by the visual analogue scale, and gait ability with walking distance were obtained at six different time points.Results: A total of 4328 medical records were examined. Four thousand two hundred and twenty-eight ageing patients received mechanical needling with sterile water injection and found the efficacy lasted up to 6 months. One hundred patients were compared with 100 patients who received lidocaine injection. Those who received lidocaine had pain returned at 3 months and 6 months post-injection.Conclusions: USG mechanical needling with sterile water injection could help relieve axial and radicular pain for at least 6 months. Removal of calcification and fibrosis as well as reduction of sensitization are all possible mechanisms.
Keywords: calcification; fibrosis; lumbar spinal stenosis; mechanical needling; pain; sterile water.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prolotherapy at Multifidus Muscle versus Mechanical Needling and Sterile Water Injection in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis.J Pain Res. 2023 Jul 18;16:2477-2486. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S417444. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37483410 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoroscopically guided caudal epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar spine stenosis.Pain Physician. 2007 Jul;10(4):547-58. Pain Physician. 2007. PMID: 17660853
-
Photobiomodulation of the dorsal root ganglion for the treatment of low back pain: A pilot study.Lasers Surg Med. 2016 Sep;48(7):653-9. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22522. Epub 2016 May 2. Lasers Surg Med. 2016. PMID: 27135465 Clinical Trial.
-
Epidural corticosteroid injections for lumbosacral radicular pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 9;4(4):CD013577. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013577. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32271952 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in pain scores and walking distance after epidural steroid injection in patients with lumbar central spinal stenosis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jun 17;101(24):e29302. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029302. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35713433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prolotherapy at Multifidus Muscle versus Mechanical Needling and Sterile Water Injection in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis.J Pain Res. 2023 Jul 18;16:2477-2486. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S417444. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37483410 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging theory of sensitization in post-stroke muscle spasticity.Front Rehabil Sci. 2023 Sep 15;4:1169087. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2023.1169087. eCollection 2023. Front Rehabil Sci. 2023. PMID: 37791371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-Articular Facet Joint Injection of Normal Saline for Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 28;59(6):1038. doi: 10.3390/medicina59061038. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37374242 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Highlights in medical and surgical rehabilitation 2021/22.Front Rehabil Sci. 2023 Jun 9;4:1219924. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2023.1219924. eCollection 2023. Front Rehabil Sci. 2023. PMID: 37383150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Machine learning prediction of extended length of stay following endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: A retrospective cohort study.Digit Health. 2025 Jul 22;11:20552076251361658. doi: 10.1177/20552076251361658. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40718407 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

