Dexpanthenol attenuates inflammatory damage and apoptosis in kidney and liver tissues of septic mice
- PMID: 35510377
- PMCID: PMC9275904
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2070585
Dexpanthenol attenuates inflammatory damage and apoptosis in kidney and liver tissues of septic mice
Abstract
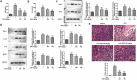
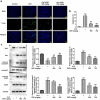
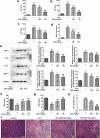
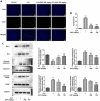
Sepsis is capable of causing systemic infections resulting in multiple organ damage. Dexpanthenol (DXP) has been reported to protect against kidney and liver injury. Therefore, this paper attempts to explore the role of DXP in sepsis-induced kidney and liver injury. A mice model of sepsis was established using the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) method. The expressions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 in the serum of mice were measured utilizing enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Additionally, the damage of kidney and liver tissues in CLP-induced mice was determined by their respective commercial kits, western blot, and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining kits. The apoptosis of kidney and liver tissues in CLP-induced mice was assessed by means of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and western blot. It was observed that DXP decreased the expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP-1 in the serum of CLP-induced mice, attenuated the functional impairment, pathological damage, inflammation, and cell apoptosis of kidney tissue. Meanwhile, DXP decreased the functional impairment of liver in CLP-induced mice, reduced the levels of inflammatory factors and antioxidant enzymes, attenuated liver pathological damage, and decreased cell apoptosis in liver tissues. In conclusion, DXP attenuates inflammatory damage and apoptosis in kidney and liver organs in a sepsis model.
Keywords: Dexpanthenol; apoptosis; inflammation; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
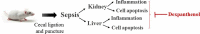
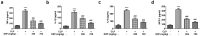
Similar articles
-
Neoastilbin ameliorates sepsis-induced liver and kidney injury by blocking the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Oct;39(10):1329-1342. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-719. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38372079
-
Inhibiting apoptosis and GSDME-mediated pyroptosis attenuates hepatic injury in septic mice.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024 Apr;754:109923. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.109923. Epub 2024 Feb 24. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38408533
-
Pioglitazone attenuates lung injury by modulating adipose inflammation.J Surg Res. 2014 Jun 15;189(2):295-303. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 24713471
-
Idebenone reduces sepsis-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in hepatocytes via RAGE/p38 signaling.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1363. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5758. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660726 Free PMC article.
-
Gadolinium Chloride Inhibits the Production of Liver Interleukin-27 and Mitigates Liver Injury in the CLP Mouse Model.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jan 29;2021:2605973. doi: 10.1155/2021/2605973. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33564275 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of dexpanthenol on 5-fluorouraci-induced nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and intestinal mucositis in rats: a clinical, biochemical, and pathological study.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2025 Feb 28;19(1):36-50. doi: 10.2478/abm-2025-0006. eCollection 2025 Feb. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2025. PMID: 40231165 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death signaling and immune regulation: new perspectives on targeted therapy for sepsis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Aug 15;30(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00784-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40817040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexpanthenol improved stem cells against cisplatin-induced kidney injury by inhibition of TNF-α, TGFβ-1, β-catenin, and fibronectin pathways.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Sep;30(9):103773. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103773. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37635837 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine receptor type 5 inhibitor maraviroc alleviates sepsis-associated liver injury by regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3655-3666. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03477-x. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39352530 Free PMC article.
-
Neoastilbin ameliorates sepsis-induced liver and kidney injury by blocking the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Oct;39(10):1329-1342. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-719. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38372079
References
-
- Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(5):581–614. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary MM, Taylor J, Eckel L. Psychopathic personality traits and cortisol response to stress: the role of sex, type of stressor, and menstrual phase. Horm Behav. 2010;58(2):250–256. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
