PEAPOD repressors modulate and coordinate developmental responses to light intensity in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 35510737
- PMCID: PMC9544094
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.18198
PEAPOD repressors modulate and coordinate developmental responses to light intensity in Arabidopsis
Abstract
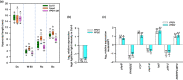
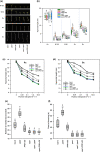
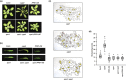
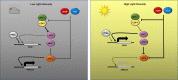
Higher plants adapt to different light intensities by altering hypocotyl elongation, stomatal density, seed size, and flowering time. Despite the importance of this developmental plasticity, knowledge of the underlying genetic and molecular mechanisms modulating and coordinating responses to light intensity remains incomplete. Here, I report that in Arabidopsis the PEAPOD (PPD) repressors PPD1 and PPD2 prevent exaggerated responses to light intensity. Genetic and transcriptome analyses, of a ppd deletion mutant and a PPD1 overexpression genotype, were used to identify how PPD repressors modulate the light signalling network. A ppd1/ppd2 deletion mutant has elongated hypocotyls, elevated stomatal density, enlarged seed, and delayed flowering, whereas overexpression of PPD1 results in the reverse. Transcription of both PPD1 and PPD2, upregulated in low light and downregulated in higher light, is activated by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4. I found PPDs modulate light signalling by negative regulation of SUPPRESSOR OF phyA-105 (SPA1) transcription. Whereas PPDs coordinate many of the responses to light intensity - hypocotyl elongation, flowering time, and stomatal density - by repression/de-repression of SPA1, PPD regulation of seed size occurs independent of SPA1. In conclusion PPD repressors modulate and coordinate developmental responses to light intensity by altering light signal transduction.
Keywords: PEAPOD; SPA1; gene regulation; light signalling; photomorphogenesis; repressor.
© 2022 The Author. New Phytologist © 2022 New Phytologist Foundation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis NF-YCs Mediate the Light-Controlled Hypocotyl Elongation via Modulating Histone Acetylation.Mol Plant. 2017 Feb 13;10(2):260-273. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.11.007. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Mol Plant. 2017. PMID: 27876642
-
PEAPOD regulates lamina size and curvature in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 29;103(35):13238-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604349103. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16916932 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis PEAPODs function with LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 to regulate lateral organ growth.J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Jun;62(6):812-831. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12841. Epub 2019 Sep 25. J Integr Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 31099089
-
Convergent regulation of PIFs and the E3 ligase COP1/SPA1 mediates thermosensory hypocotyl elongation by plant phytochromes.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018 Oct;45(Pt A):188-203. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2018.09.006. Epub 2018 Sep 29. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30273926 Review.
-
Signaling mechanisms of plant cryptochromes in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Plant Res. 2016 Mar;129(2):137-48. doi: 10.1007/s10265-015-0782-z. Epub 2016 Jan 25. J Plant Res. 2016. PMID: 26810763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The PEAPOD repressor complex in Arabidopsis stomatal development.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jul 23;16:1641102. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1641102. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40772046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Non-JAZ TIFY Protein TIFY8 of Arabidopsis thaliana Interacts with the HD-ZIP III Transcription Factor REVOLUTA and Regulates Leaf Senescence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 4;24(4):3079. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043079. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834490 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic control of stem elongation in common bean and the influence of age and flowering time.Theor Appl Genet. 2025 Aug 21;138(9):222. doi: 10.1007/s00122-025-04996-8. Theor Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 40839248 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental validation of the mechanism of stomatal development diversification.J Exp Bot. 2023 Sep 29;74(18):5667-5681. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad279. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 37555400 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide insights into the nomenclature, evolution and expression of tobacco TIFY/JAZ genes.Planta. 2025 Apr 4;261(5):103. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04676-3. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40183817
References
-
- Al‐Sady B, Ni W, Kircher S, Schäfer E, Quail PH. 2006. Photoactivated phytochrome induces rapid PIF3 phosphorylation prior to proteasome‐mediated degradation. Molecular Cell 23: 439–446. - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Meng Y, Huang D, Qi Y, Chen M. 2011. Origin and evolutionary analysis of the plant‐specific TIFY transcription factor family. Genomics 98: 128–136. - PubMed
-
- Balcerowicz M, Fittinghoff K, Wirthmueller L, Maier A, Fackendahl P, Fiene G, Koncz C, Hoecker U. 2011. Light exposure of Arabidopsis seedlings causes rapid de‐stabilization as well as selective post‐translational inactivation of the repressor of photomorphogenesis SPA2. The Plant Journal 65: 712–723. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

