Comparative analysis of patients' survival on hemodialysis vs. peritoneal dialysis and identification of factors associated with death
- PMID: 35510838
- PMCID: PMC10139729
- DOI: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2021-0242en
Comparative analysis of patients' survival on hemodialysis vs. peritoneal dialysis and identification of factors associated with death
Abstract
Introduction: There are several studies comparing the outcomes of patients treated with peritoneal dialysis (PD) and hemodialysis (HD), and most are divergent.
Methods: This is a cohort study that followed patients with incident PD and HD in a planned and unplanned way, in a dialysis unit of the HCFMB from 01/2014 to 01/2019, until the outcome. We collected clinical and laboratory data. The PD and HD groups, death and non-death outcomes, were compared using the chi-square test for categorical variables and t-test, or Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables. Kaplan Meier curve and log-rank test were used for survival. Multivariate analysis was performed using the Cox regression. The significant difference was p < 0.05.
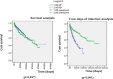
Results: We had 592 patients, 290 treated by HD and 302 by PD. The mean age was 59.9 ± 16.8, with a predominance of males (56.3%), the main underlying disease was diabetes (45%); 29% of the patients died. There was no difference in the survival of patients treated by HD and PD. The oldest age (1.018 (95% CI 1.000-1.037; p=0.046)) was identified as a risk factor for death, while the highest number of infection-free days (0.999 (95% CI 0.999-1.000; p=0.003 )) as a protective factor.
Conclusion: The analysis reinforced that the survival of patients on HD and PD was similar. Higher age and shorter infection-free time were associated with death.
Introdução:: Há vários estudos que comparam os desfechos de pacientes tratados por diálise peritoneal (DP) e hemodiálise (HD), e a maioria é divergente.
Métodos:: Estudo de coorte que acompanhou pacientes incidentes em DP e HD de modo planejado e não planejado em unidade de diálise do HCFMB de 01/2014 a 01/2019, até o desfecho. Foram coletados dados clínicos e laboratoriais. Comparou-se os grupos DP e HD, óbito e não óbito, por meio do teste qui-quadrado para variáveis categóricas e teste t ou Mann-Whitney para as contínuas. Curva de Kaplan Meier e log-rank test foram utilizados para a sobrevida. A análise multivariada foi realizada por Regressão de Cox. A diferença significante foi de p < 0,05.
Resultados:: Foram estudados 592 pacientes, 290 tratados por HD e 302 por DP. A média de idade foi de 59,9 ± 16,8, com predomínio de sexo masculino (56,3%), principal doença de base, diabetes (45%). Óbito ocorreu em 29% dos pacientes. Não houve diferença na sobrevida de pacientes tratados por HD e DP. A maior idade (1,018 (IC 95% 1,000-1,037; p=0,046)) foi identificada como fator de risco para o óbito, enquanto a maior quantidade de dias livres de infecção (0,999 (IC 95% 0,999-1,000; p=0,003)), como fator de proteção.
Conclusão:: A análise reforçou que a sobrevida dos pacientes em HD e DP é semelhante. Foram associados ao óbito a maior idade e o menor tempo livre de infecção.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Peritoneal dialysis: why not?J Bras Nefrol. 2023 Jan-Mar;45(1):1-2. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2023-E001en. J Bras Nefrol. 2023. PMID: 37015051 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Penico MG, Paulo Koah. Cartilha dia Mundial do Rim. S. l: Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia; mar. 2016. [Acesso em: 22 set. 2019]. Disponível em: https://arquivos.sbn.org.br/uploads/dmr2016_cartilha.pdf .
-
- Censo da Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia. 2017. [Acesso em: 04, Junho, 2019]. Disponível em < www.sbn.org.br>.
-
- Beraldo N. Saúde alerta para prevenção e diagnóstico precoce da Doença Renal Crônica. S. l: Ministério da Saúde; mar. 2019. [Acesso em: 22 set 2019]. Disponível em: http://www.saude.gov.br/noticias/agencia-saude/45291-ministerio-da-saude... .
-
- Niang A; A, Iyengar A, Luychx V. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension. S. l: nov. 2018. Hemodialysis versus peritoneal dialysis in resource-limited setting; pp. 463–471. Disponível em: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30148722 . - PubMed
-
- Thiery A, Séverac F, Hannedouche T, Couchoud C, Do VH, Tiple A, et al. Survival advantage of planned haemodialysis over peritoneal dialysis: A cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical