Flexible and multifaceted: the plasticity of renin-expressing cells
- PMID: 35511367
- PMCID: PMC9338909
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-022-02694-8
Flexible and multifaceted: the plasticity of renin-expressing cells
Abstract
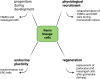
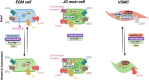
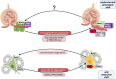
The protease renin, the key enzyme of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, is mainly produced and secreted by juxtaglomerular cells in the kidney, which are located in the walls of the afferent arterioles at their entrance into the glomeruli. When the body's demand for renin rises, the renin production capacity of the kidneys commonly increases by induction of renin expression in vascular smooth muscle cells and in extraglomerular mesangial cells. These cells undergo a reversible metaplastic cellular transformation in order to produce renin. Juxtaglomerular cells of the renin lineage have also been described to migrate into the glomerulus and differentiate into podocytes, epithelial cells or mesangial cells to restore damaged cells in states of glomerular disease. More recently, it could be shown that renin cells can also undergo an endocrine and metaplastic switch to erythropoietin-producing cells. This review aims to describe the high degree of plasticity of renin-producing cells of the kidneys and to analyze the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Erythropoietin; Phenotypic transformation; Regeneration; Renal interstitial cells; Renin; Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bachmann S, Le Hir M, Eckardt KU. Co-localization of erythropoietin mRNA and ecto-5’-nucleotidase immunoreactivity in peritubular cells of rat renal cortex indicates that fibroblasts produce erythropoietin. J Histochem Cytochem Off J Histochem Soc. 1993;41:335–341. doi: 10.1177/41.3.8429197. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broeker KAE, Fuchs MAA, Schrankl J, Kurt B, Nolan KA, Wenger RH, Kramann R, Wagner C, Kurtz A. Different subpopulations of kidney interstitial cells produce erythropoietin and factors supporting tissue oxygenation in response to hypoxia in vivo. Kidney Int. 2020;98:918–931. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.04.040. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

