Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to therapeutics
- PMID: 35511596
- PMCID: PMC9465638
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac028
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to therapeutics
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM or T2D) is a devastating metabolic abnormality featured by insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia. T2D provokes unique metabolic changes and compromises cardiovascular geometry and function. Meanwhile, T2D increases the overall risk for heart failure (HF) and acts independent of classical risk factors including coronary artery disease, hypertension, and valvular heart diseases. The incidence of HF is extremely high in patients with T2D and is manifested as HF with preserved, reduced, and midrange ejection fraction (HFpEF, HFrEF, and HFmrEF, respectively), all of which significantly worsen the prognosis for T2D. HFpEF is seen in approximately half of the HF cases and is defined as a heterogenous syndrome with discrete phenotypes, particularly in close association with metabolic syndrome. Nonetheless, management of HFpEF in T2D remains unclear, largely due to the poorly defined pathophysiology behind HFpEF. Here, in this review, we will summarize findings from multiple preclinical and clinical studies as well as recent clinical trials, mainly focusing on the pathophysiology, potential mechanisms, and therapies of HFpEF in T2D.
Keywords: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; pathophysiology; therapies; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© The Author(s) (2022). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, CEMCS, CAS.
Figures
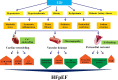
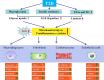
References
-
- Ananthram M.G., Gottlieb S.S. (2021). Renal dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Heart Fail. Clin. 17, 357–367. - PubMed
-
- Anker S.D., Butler J., Filippatos G.S.et al. (2019). Evaluation of the effects of sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition with empagliflozin on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure and a preserved ejection fraction: rationale for and design of the EMPEROR-Preserved Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 21, 1279–1287. - PubMed
-
- Atila Uslu G., Uslu H. (2022). Evaluating the effects of Juglans regia L. extract on hyperglycaemia and insulin sensitivity in experimental type 2 diabetes in rat. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 128, 121–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

