[IgG4-related disease with nasopharyngeal malignancy-like manifestations]
- PMID: 35511623
- PMCID: PMC10128187
- DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.011
[IgG4-related disease with nasopharyngeal malignancy-like manifestations]
Abstract
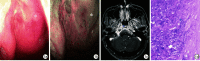
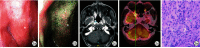
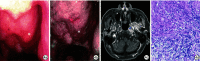
Objective:The purpose of this article was to discuss the clinical features and imaging characteristics of IgG4-related disease(IgG4-RD) in order to identify nasopharyngeal IgG4-RD at an early stage. Methods:The basic information of the patients, including age, sex, symptoms, disease duration and treatment process, was collected through the electronic case system. Laboratory tests including nasal endoscopy, EBV levels, IgG4 levels and C-reactive protein levels were recorded during hospitalization and outpatient follow-up. All radiological imaging and postoperative pathology data are collected, analyzed and summarized. Results:All patients underwent partial excisional biopsy of the lesion. The pathological findings showed inflammatory granulomatous and fibrous tissue hyperplasia with a high infiltration of lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils, and immunohistochemistry examination showed IgG4+ plasma cells were more than 10 per high magnification field. Combining medical history, imaging, serological findings and relevant treatment, all four patients were diagnosed with IgG4-associated disease. And their symptoms improved significantly after hormonal and immunosuppressive treatment. Conclusion: IgG4-RD has a highly similar clinical presentation with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Differentiation from IgG4-RD should be considered for those pathology cannot be clarified by multiple biopsies. Timely diagnosis of IgG4-RD is important to prevent secondary organ damage in patients with active disease.
目的:探讨IgG4相关疾病(IgG4-RD)的临床特征和影像学特征,提高鼻咽IgG4-RD早期的诊断能力,减少误诊与漏诊。 方法:通过电子病例系统采集患者基本信息,包括年龄、性别、症状、病程和诊疗过程。记录患者住院期间及门诊随诊的实验室检查资料,包括鼻内镜检查、EB病毒水平、IgG4水平及C反应蛋白水平等。对患者的CT、MRI以及PET-CT特征进行总结分析,并收集所有患者的病理和免疫组织化学结果。 结果:4例患者均行病灶部分切除活检术,病理结果显示炎性肉芽组织和纤维组织增生,淋巴细胞、浆细胞和中性粒细胞浸润较多,免疫组织化学IgG4+浆细胞每高倍视野均>10个。结合病史、影像学检查、血清学结果及相关治疗,最终诊断为IgG4-RD,经激素和免疫抑制治疗后症状均有明显改善。 结论:IgG4-RD与鼻咽癌的临床表现高度相似,对伴有似鼻咽癌症状且多次活检无法明确病理的患者,需要与IgG4-RD进行鉴别,及时诊断IgG4-RD对预防活动性疾病患者继发性脏器损害具有重要意义。.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; diagnose; nasopharyngeal neoplasms; rare diseases.
Copyright© by the Editorial Department of Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article and the planning committee members and staff have no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IgG4-related disease with nasopharyngeal malignancy-like manifestations.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1322159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1322159. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966645 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal manifestation of immunoglobulin G4-related disease: clarification through a multicenter survey.J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul;53(7):845-853. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1420-4. Epub 2017 Dec 8. J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29222587
-
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease of the stomach - a challenging differential diagnosis in suspected gastric cancer.Z Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov;57(11):1298-1303. doi: 10.1055/a-1013-4437. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Z Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31739375 English.
-
IgG4-Related Disease With Testicular Involvement: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 10;12:717902. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.717902. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34447384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease Manifesting as Isolated, Typical, and Nontypical Gastroesophageal Lesion: A Research of Literature Review.Digestion. 2020;101(5):506-521. doi: 10.1159/000501513. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Digestion. 2020. PMID: 31291621 Review.
Cited by
-
IgG4-related disease with nasopharyngeal malignancy-like manifestations.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1322159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1322159. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38966645 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Elevated IgG4 in Patients with Nasopharynx and Laryngopharynx Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Jan;77(1):626-634. doi: 10.1007/s12070-024-05189-3. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40066385
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous