Comparison of suture anchor penetration rate between navigation-assisted and traditional shoulder arthroscopic capsulolabral repair
- PMID: 35511770
- PMCID: PMC9070905
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267943
Comparison of suture anchor penetration rate between navigation-assisted and traditional shoulder arthroscopic capsulolabral repair
Abstract
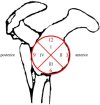
Proper placement of suture anchors is an important step in Bankart repair as improper placement can lead to failure. Concern surrounding suture anchor placement inspired the use navigation systems in shoulder arthroscopy. We aimed to demonstrate the technological advantage of using the O-arm (Medtronic Navigation, Denver, CO, USA) image guidance system to provide real-time images during portal and anchor placements in shoulder arthroscopy. Consecutive patients (from July to October 2014) who were admitted for arthroscopic capsulolabral repair surgeries were included. Ten patients were randomly enrolled in the navigation group and 10 in the traditional group. The glenoid was divided into four zones, and the penetration rates in each zone were compared between the two groups. In zone III, the most inferior region of the glenoid, the penetration rate was 40.9% in the traditional group and 15.7% in the navigation group (P = 0.077), demonstrating a trend toward improved accuracy of anchor placement with the aid of the navigation system; however, this was not statistically significant. Average surgical time in the navigation and traditional groups was 177.6±40.2 and 117.7±17.6 mins, respectively. American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons Shoulder Scores showed no difference before and 6 months after surgery. This pilot study showed a trend toward decreased penetration rate in O-arm-navigated capsulolabral repair surgeries and decreased risks of implant misplacement; however, possibly due to the small sample size, the difference was not statistically significant. Further large-scale studies are needed to confirm the possible benefit of the navigation system. Even with the use of navigation systems, there were still some penetrations in zone III of the glenoid. This penetration may be attributed to the micro-motion of the acromioclavicular joint. Although the navigation group showed a significant increase in surgical time, with improvements in instrument design, O-arm-navigated arthroscopy will gain popularity in clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beach Chair Versus Lateral Decubitus Position: Differences in Suture Anchor Position and Number During Arthroscopic Anterior Shoulder Stabilization.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jul;49(8):2020-2026. doi: 10.1177/03635465211013709. Epub 2021 May 21. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 34019439
-
Postoperative Recurrence of Instability Due to New Anterior Glenoid Rim Fractures After Arthroscopic Bankart Repair.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Oct;45(12):2840-2848. doi: 10.1177/0363546517714476. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28728432
-
Freehand versus navigated glenoid anchor positioning in anterior labral repair.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011 Sep;19(9):1554-7. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1360-5. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. PMID: 21222107
-
"Postage Stamp" Fractures: A Systematic Review of Patient and Suture Anchor Profiles Causing Anterior Glenoid Rim Fractures After Bankart Repair.Arthroscopy. 2019 Aug;35(8):2501-2508.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2019.02.047. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 31395192
-
A meta-analysis of open versus arthroscopic Bankart repair using suture anchors.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010 Dec;18(12):1742-7. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1093-5. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010. PMID: 20237768 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

