Evidence-based practice and its associated factors among point-of-care nurses working at the teaching and specialized hospitals of Northwest Ethiopia: A concurrent study
- PMID: 35511810
- PMCID: PMC9070954
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267347
Evidence-based practice and its associated factors among point-of-care nurses working at the teaching and specialized hospitals of Northwest Ethiopia: A concurrent study
Abstract
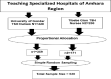
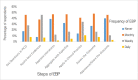
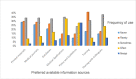
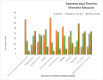
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the application of the best scientific evidence for clinical decision-making in professional patient care. In Ethiopia, the majority of nursing care is based on experience, tradition, intuition, common sense, and untested hypotheses. Evidence-based clinical practice has the potential to increase the quality of healthcare services while also lowering costs and increasing clinical outcomes. An institutional-based concurrent study design method of quantitative and qualitative research was conducted from Feb. 30 to Apr. 20, 2020. Systematic random sampling and purposive sampling techniques were used to select the study participants for the quantitative and qualitative analyses, respectively. To collect quantitative data, a pretested, structured, and self-administered questionnaire was used, and to collect qualitative data, an in-depth interview guided by questions was used. EBP was found to be significantly associated with educational level (AOR = 2.15, CI (1.15-4.02)), administrative support for EBP (AOR = 1.89, CI (1.22-2.91)), attitude toward EBP (AOR = 1.80, CI (1.24-2.62)), and preference of available information sources (AOR: 2.32, CI (1.58-3.39). The four main themes that emerged from the conventional content data analysis were the advantages of EBP application, barriers to EBP implementation, enabling factors for EBP, and evidence sharing. According to the findings of this study, only a few nurses used EBP at a high level. The implementation of EBP was positively associated with educational level, attitude toward EBP, administrative support, and the availability of information resources, as confirmed by the qualitative study. There must be an intervention program to facilitate the implementation of evidence in nursing practice by stakeholders to improve and increase the efficacy of practicing EBP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
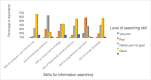
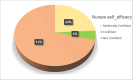
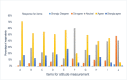
Similar articles
-
Determinants of evidence-based practice among health care professionals in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 9;18(11):e0293902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293902. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37943797 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional study of evidence-based practice and association factors among nurses in public health facilities of Dessie city, Northeast Ethiopia.Front Public Health. 2025 Mar 11;13:1540388. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1540388. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40135155 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based practice among health professionals in hospitals of Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2017 Dec;15(4):161-170. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000111. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2017. PMID: 28509809
-
Evidence-based practice an d associated factors among health professionals working at public hospitals in South Wollo zone, Ethiopia, 2023: a mixed study.BMJ Open. 2025 Mar 3;15(3):e091786. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091786. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40032394 Free PMC article.
-
Limited Evidence to Fully Determine the Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice by Healthcare Providers in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Evid Based Med. 2025 Jun;18(2):e70032. doi: 10.1111/jebm.70032. J Evid Based Med. 2025. PMID: 40375060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nurses' perception of the hospitals' culture and readiness of evidence-based practise integration in the hospital's system in western Ethiopia.BMC Nurs. 2024 Feb 7;23(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-01741-2. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38321447 Free PMC article.
-
Nurses' implementation of evidence based practice in nursing process and its associated factors in South Wollo Zone public hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia: a mixed method study.BMC Nurs. 2024 Oct 24;23(1):782. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02444-4. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39449058 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of evidence-based practice among health care professionals in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 9;18(11):e0293902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293902. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37943797 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Nursing Interventions in Women With Gestational Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nurs Health Sci. 2025 Mar;27(1):e70074. doi: 10.1111/nhs.70074. Nurs Health Sci. 2025. PMID: 40064480 Free PMC article.
-
PubMed4Hh: A Point-of-Care Mobile App for Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Support for Nurse Residents in Maryland.Comput Inform Nurs. 2023 Dec 1;41(12):983-992. doi: 10.1097/CIN.0000000000001063. Comput Inform Nurs. 2023. PMID: 38062547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melnyk BM, Fineout-Overholt E, editors. Evidence-based practice in nursing & healthcare: A guide to best practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. 208–224
-
- Banning MJJo CN. Conceptions of evidence, evidence-based medicine, evidence-based practice, and their use in nursing: independent nurse prescribers’ views. 2015; 14 (4):411–417. - PubMed
-
- Tranmer Ja; Squires S, Brazil K, Gerlach J, Johnson J, Muisiner D, et al.. Factors that influence evidence-based decision-making. 1998; 5:3–92.
-
- Mokhtar IA, Majid S, Foo S, Zhang X, Zheng Y-L, Chang Y-K, et al.. Evidence-based practice and related information literacy skills of nurses in Singapore: an exploratory case study Malaysian Journal of Literacy and Information Science, 2012; 18(1): 12–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

