MicroRNA candidate miRcand137 in apple is induced by Botryosphaeria dothidea for impairing host defense
- PMID: 35512059
- PMCID: PMC9237668
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiac171
MicroRNA candidate miRcand137 in apple is induced by Botryosphaeria dothidea for impairing host defense
Abstract
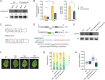
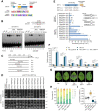
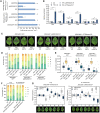
MicroRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene silencing is a master gene regulatory pathway in plant-pathogen interactions. The differential accumulation of miRNAs among plant varieties alters the expression of target genes, affecting plant defense responses and causing resistance differences among varieties. Botryosphaeria dothidea is an important phytopathogenic fungus of apple (Malus domestica). Malus hupehensis (Pamp.) Rehder, a wild apple species, is highly resistant, whereas the apple cultivar "Fuji" is highly susceptible. Here, we identified a 22-nt miRNA candidate named miRcand137 that compromises host resistance to B. dothidea infection and whose processing was affected by precursor sequence variation between M. hupehensis and "Fuji." miRcand137 guides the direct cleavage of and produced target-derived secondary siRNA against Ethylene response factor 14 (ERF14), a transcriptional activator of pathogenesis-related homologs that confers disease resistance to apple. We showed that miRcand137 acts as an inhibitor of apple immunity by compromising ERF14-mediated anti-fungal defense and revealed a negative association between miRcand137 expression and B. dothidea sensitivity in both resistant and susceptible apples. Furthermore, MIRCAND137 was transcriptionally activated by the invading fungi but not by the fungal elicitor, implying B. dothidea induced host miRcand137 as an infection strategy. We propose that the inefficient miRcand137 processing in M. hupehensis decreased pathogen-initiated miRcand137 accumulation, leading to higher resistance against B. dothidea.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2022. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Host-induced gene silencing in wild apple germplasm Malus hupehensis confers resistance to the fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea.Plant J. 2024 May;118(4):1174-1193. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16664. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 38430515
-
Malus hupehensis miR168 Targets to ARGONAUTE1 and Contributes to the Resistance against Botryosphaeria dothidea Infection by Altering Defense Responses.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;58(9):1541-1557. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx080. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28633325
-
Apple ethylene response factor MdERF11 confers resistance to fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea.Plant Sci. 2020 Feb;291:110351. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110351. Epub 2019 Nov 23. Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 31928678
-
MicroRNA397b negatively regulates resistance of Malus hupehensis to Botryosphaeria dothidea by modulating MhLAC7 involved in lignin biosynthesis.Plant Sci. 2020 Mar;292:110390. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110390. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32005395
-
Botryosphaeria dothidea: a latent pathogen of global importance to woody plant health.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 May;18(4):477-488. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12495. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27682468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic weapons of plants against fungal pathogens.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Mar 6;24(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04829-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38443788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis DREB26/ERF12 and its close relatives regulate cuticular wax biosynthesis under drought stress condition.Plant J. 2024 Dec;120(5):2057-2075. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17100. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 39466828 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of microRNAs in horticultural plant disease resistance.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 27;14:1137471. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1137471. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36923786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Resistance to Alternaria alternata Apple Pathotype in Apple by Alternative Splicing of Transcription Factor MdMYB6-like.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 15;25(8):4353. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084353. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673937 Free PMC article.
-
MdPOB1L Positively Regulates Disease Resistance Against Botryosphaeria dothidea by Manipulating MdNPR1 Protein Stability in Malus domestica.Mol Plant Pathol. 2025 Aug;26(8):e70129. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70129. Mol Plant Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40773493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akagi A, Dandekar AM, Stotz HU (2011) Resistance of Malus domestica fruit to Botrytis cinerea depends on endogenous ethylene biosynthesis. Phytopathology 101: 1311–1321 - PubMed
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC (2005) microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121: 207–221 - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ (2008) Evolution of microRNAs and their targets: are all microRNAs biologically relevant? Biochim Biophys Acta 1779: 725–734 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

