Development of Temporal Model for Forecasting of Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidopetra) Using Arima and Artificial Neural Networks
- PMID: 35512683
- PMCID: PMC9071552
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/ieac019
Development of Temporal Model for Forecasting of Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae: Lepidopetra) Using Arima and Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
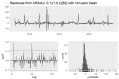
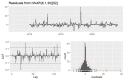
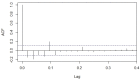
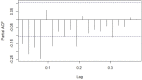
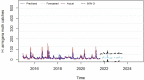
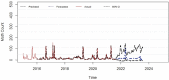
Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Noctuidae: Lepidopetra) is a polyphagous pest of major crops grown in India. To prevent the damage caused by H. armigera farmers rely heavily on insecticides of diverse groups on a regular basis which is not a benign practice, environmentally and economically. To provide more efficient and accurate information on timely application of insecticides, this research was aimed to develop a forecast model to predict population dynamics of pod borer using Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). The data used in this study were collected from the randomly installed sex pheromone traps at International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-arid Tropics (ICRISAT), Patancheru, Hyderabad. Several ARIMA (p, d, q) (P, D, Q) and ANN models were developed using the historical trap catch data. ARIMA model (1,0,1), (1,0,2) with minimal BIC, RMSE, MAPE, MAE, and MASE values and higher R2 value (0.53) was selected as the best ARIMA fit model, and neural network (7-30-1) was found to be the best fit to predict the catches of male moths of pod borer from September 2021 to August 2023. A comparative analysis performed between the ARIMA and ANN, shows that the ANN based on feed forward neural networks is best suited for effective pest prediction. With the developed ARIMA model, it would be easier to predict H. armigera adult population dynamics round the year and timely intervention of control measures can be followed by appropriate decision-making schedule for insecticide application.
Keywords: H. armigera; ARIMA; Artificial Neural Networks; forecast.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Entomological Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Adebiyi, A. A., Adewumi A., and OAyo C. K.. . 2014. Comparison of ARIMA and artificial neural networks models for stock price prediction. J. Appl. Math. 2014: 1–7. doi:10.1155/2014/614342. - DOI
-
- Agrawal, R., and Mehta S. C.. . 2007. Weather based forecasting of crop yields, pests and diseases-IASRI models. J. Ind. Soc. Agril. Stat. 61: 255–263.
-
- Areef, M., and Radha Y.. . 2020. Application of GARCH and ANN models for potato price forecasting: a case study of Bangalore market, Karnataka state. Indian J. Agric. Mark. 34: 44–52.
-
- Armes, N. J., Jadhav D. R., and DeSouza K. R.. . 1996. A survey of insecticide resistance in Helicoverpa armigera in the Indian subcontinent. Bull. Entomol. Res. 86: 499–514.
-
- Boopathi, T., Singh S. B., Manju T., Ramakrishna Y., Akoijam R. S., Chowdhury S., Singh N. H., and Ngachan S. V.. . 2015. Development of temporal modelling for forecasting and prediction of the incidence of lychee, Tessaratoma papillosa (Hemiptera: Tessaratomidae), using time-series (ARIMA) analysis. J. Insect Sci. 15: 55.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

