Platelet Function and Genotype after DES Implantation in East Asian Patients: Rationale and Characteristics of the PTRG-DES Consortium
- PMID: 35512743
- PMCID: PMC9086699
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.5.413
Platelet Function and Genotype after DES Implantation in East Asian Patients: Rationale and Characteristics of the PTRG-DES Consortium
Abstract
Purpose: Platelet function test (PFT) results and genotype hold unique prognostic implications in East Asian patients. The aim of the PTRG-DES (Platelet function and genoType-Related long-term proGnosis in Drug-Eluting Stent-treated Patients with coronary artery disease) consortium is to assess the clinical impact thereof on long-term clinical outcomes in Korean patients with coronary artery disease during dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) including clopidogrel.
Materials and methods: Searching publications on the PubMed, we reviewed clopidogrel treatment studies with PFT and/or genotype data for potential inclusion in this study. Lead investigators were invited to share PFT/genotype results, patient characteristics, and clinical outcomes to evaluate relationships among them.
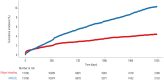
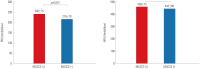
Results: Nine registries from 32 academic centers participated in the PTRG-DES consortium, contributing individual patient data from 13160 patients who underwent DES implantation between July 2003 and August 2018. The PTRG-PFT cohort was composed of 11714 patients with available VerifyNow assay results. Platelet reactivity levels reached 218±79 P2Y12 reaction units (PRU), and high on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity based on a consensus-recommended cutoff (PRU >208) was observed in 55.9%. The PTRG-Genotype cohort consisted of 8163 patients with candidate genotypes related with clopidogrel responsiveness. Of those with cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 genotype, frequencies of carrying one and two loss-of-function allele (s) (*2 or *3) were 47.9% (intermediate metabolizers) and 14.2% (poor metabolizers), respectively.
Conclusion: The PTRG-DES consortium highlights unique values for on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity and CYP2C19 phenotype that may be important to developing optimal antiplatelet regimens in East Asian patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04734028.
Keywords: East Asia; coronary artery disease; drug-eluting stent; genotype; platelet function.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Jeong has received honoraria for lectures from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi-Aventis, Han-mi Pharmaceuticals, and Yuhan Pharmaceuticals, as well as research grants or support from Yuhan Pharmaceuticals and U&I Corporation. Dr. Song has received honoraria for lectures from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi-Aventis, Bayer Korea, and Samjin Pharmaceutical. Dr. Joo has received honoraria for lectures from AstraZeneca, Hanmi, Samjin, Dong-A, HK inno. N Pharmaceuticals, and DIO Medical Ltd. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Bittl JA, Brindis RG, Fihn SD, Fleisher LA, et al. 2016 ACC/AHA guideline focused update on duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:1082–1115. - PubMed
-
- Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Byrne RA, Collet JP, Costa F, Jeppsson A, et al. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: the Task Force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur Heart J. 2017;39:213–260. - PubMed
-
- Sibbing D, Aradi D, Alexopoulos D, Ten Berg J, Bhatt DL, Bonello L, et al. Updated expert consensus statement on platelet function and genetic testing for guiding P2Y12 receptor inhibitor treatment in percutaneous coronary intervention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1521–1537. - PubMed
-
- Kim HK, Tantry US, Smith SC, Jr, Jeong MH, Park SJ, Kim MH, et al. The East Asian paradox: an updated position statement on the challenges to the current antithrombotic strategy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Thromb Haemost. 2021;121:422–432. - PubMed
-
- Levine GN, Jeong YH, Goto S, Anderson JL, Huo Y, Mega JL, et al. Expert consensus document: World Heart Federation expert consensus statement on antiplatelet therapy in East Asian patients with ACS or undergoing PCI. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014;11:597–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

