Severity-Adjusted Dexamethasone Dosing and Tocilizumab Combination for Severe COVID-19
- PMID: 35512745
- PMCID: PMC9086692
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.5.430
Severity-Adjusted Dexamethasone Dosing and Tocilizumab Combination for Severe COVID-19
Abstract
Purpose: Real-world experience with tocilizumab in combination with dexamethasone in patients with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) needs to be investigated.
Materials and methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted to evaluate the effect of severity-adjusted dosing of dexamethasone in combination with tocilizumab for severe COVID-19 from August 2020 to August 2021. The primary endpoint was 30-day clinical recovery, which was defined as no oxygen requirement or referral after recovery.
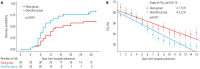
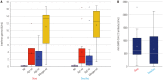
Results: A total of 66 patients were evaluated, including 33 patients in the dexamethasone (Dexa) group and 33 patients in the dexamethasone plus tocilizumab (DexaToci) group. The DexaToci group showed a statistically significant benefit in 30-day clinical recovery, compared to the Dexa group (p=0.024). In multivariable analyses, peak FiO2 within 3 days and tocilizumab combination were consistently significant for 30-day recovery (all p<0.05). The DexaToci group showed a significantly steeper decrease in FiO2 (-4.2±2.6) than the Dexa group (-2.7±2.6; p=0.021) by hospital day 15. The duration of oxygen requirement was significantly shorter in the DexaToci group than the Dexa group (median, 10.0 days vs. 17.0 days; p=0.006). Infectious complications and cellular and humoral immune responses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the convalescence stage were not different between the two groups.
Conclusion: A combination of severity-adjusted dexamethasone and tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 improved clinical recovery without increasing infectious complications or hindering the immune response against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dexamethasone; immune response; tocilizumab.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

