miR-486 is essential for muscle function and suppresses a dystrophic transcriptome
- PMID: 35512829
- PMCID: PMC9087951
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202101215
miR-486 is essential for muscle function and suppresses a dystrophic transcriptome
Abstract
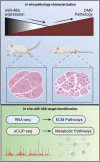
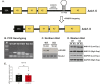
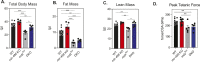
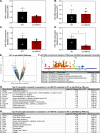
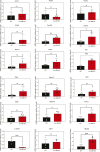
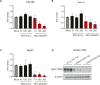
miR-486 is a muscle-enriched microRNA, or "myomiR," that has reduced expression correlated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). To determine the function of miR-486 in normal and dystrophin-deficient muscles and elucidate miR-486 target transcripts in skeletal muscle, we characterized mir-486 knockout mice (mir-486 KO). mir-486 KO mice developed disrupted myofiber architecture, decreased myofiber size, decreased locomotor activity, increased cardiac fibrosis, and metabolic defects were exacerbated in mir-486 KO:mdx 5cv (DKO) mice. To identify direct in vivo miR-486 muscle target transcripts, we integrated RNA sequencing and chimeric miRNA eCLIP sequencing to identify key transcripts and pathways that contribute towards mir-486 KO and dystrophic disease pathologies. These targets included known and novel muscle metabolic and dystrophic structural remodeling factors of muscle and skeletal muscle contractile transcript targets. Together, our studies identify miR-486 as essential for normal muscle function, a driver of pathological remodeling in dystrophin-deficient muscle, a useful biomarker for dystrophic disease progression, and highlight the use of multiple omic platforms to identify in vivo microRNA target transcripts.
© 2022 Samani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-146a deficiency does not aggravate muscular dystrophy in mdx mice.Skelet Muscle. 2019 Aug 14;9(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13395-019-0207-0. Skelet Muscle. 2019. PMID: 31412923 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-486-dependent modulation of DOCK3/PTEN/AKT signaling pathways improves muscular dystrophy-associated symptoms.J Clin Invest. 2014 Jun;124(6):2651-67. doi: 10.1172/JCI73579. Epub 2014 May 1. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24789910 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Notch signalling in skeletal muscles from mdx and dko dystrophic mice and patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Exp Physiol. 2014 Apr;99(4):675-87. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.077255. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Exp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24443351
-
Lack of miR-378 attenuates muscular dystrophy in mdx mice.JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):e135576. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.135576. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32493839 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker Potential of Extracellular miRNAs in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Nov;23(11):989-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28988850 Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating miR-29c, miR-195, and miR-486 Are Objective Indicators to Determine the Moderate Intensity of Resistance Exercise.Cureus. 2024 Dec 22;16(12):e76212. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76212. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39845226 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles and Duchenne muscular dystrophy pathology: Modulators of disease progression.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 14;14:1130063. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1130063. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36891137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of microRNAs in Skeletal Muscle of Intrauterine Growth-Restricted Pigs.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;14(7):1372. doi: 10.3390/genes14071372. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510277 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle-enriched microRNA-486-mediated regulation of muscular atrophy and exercise.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 Nov;80(4):795-809. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01043-w. Epub 2024 Sep 2. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39222208 Review.
-
Time-series transcriptomics reveals distinctive mRNA expression dynamics associated with gene ontology specificity and protein expression in skeletal muscle after electrical stimulation-induced resistance exercise.FASEB J. 2024 Nov 30;38(22):e70153. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401420RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39545720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander MS, Casar JC, Motohashi N, Vieira NM, Eisenberg I, Marshall JL, Gasperini MJ, Lek A, Myers JA, Estrella EA, et al. (2014) MicroRNA-486-dependent modulation of DOCK3/PTEN/AKT signaling pathways improves muscular dystrophy-associated symptoms. J Clin Invest 124: 2651–2667. 10.1172/JCI73579 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander MS, Kawahara G, Motohashi N, Casar JC, Eisenberg I, Myers JA, Gasperini MJ, Estrella EA, Kho AT, Mitsuhashi S, et al. (2013) MicroRNA-199a is induced in dystrophic muscle and affects WNT signaling, cell proliferation, and myogenic differentiation. Cell Death Differ 20: 1194–1208. 10.1038/cdd.2013.62 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P2C HD086851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR074006/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR071133/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083300/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD095897/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS120812/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS095775/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM140710/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F99 NS118718/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL141620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
