HPLC-Based Automated Synthesis of Glycans in Solution
- PMID: 35513346
- PMCID: PMC9403992
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202201180
HPLC-Based Automated Synthesis of Glycans in Solution
Abstract
As the 21st century unfolds with rapid changes, new challenges in research and development emerge. These new challenges prompted us to repurpose our HPLC-A platform that was previously used in solid phase glycan synthesis to a solution phase batch synthesis described herein. The modular character of HPLC allows for implementing new attachments. To enable sequential synthesis of multiple oligosaccharides with the single press of a button, we supplemented our system with a four-way split valve and an automated fraction collector. This enabled the operator to load all reagents and all reactants in the autosampler, press the button to start the repetitive automation sequence, leave the lab, and upon return find products of multiple reactions ready for purification, analysis, and subsequent application.
Keywords: automation; glycans; glycosylation; oligosaccharides; synthesis.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

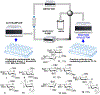
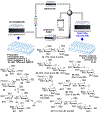
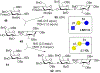
References
-
- Toy PH, Lam Y in Solid-phase organic synthesis, Vol. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, 2012.
-
- Tanaka H, Matoba N, Tsukamoto H, Takimoto H, Yamada H, Takahashi T, Synlett 2005, 824–828;
- Machida K, Hirose Y, Fuse S, Sugawara T, Takahashi T, Chem. Pharm. Bull 2010, 58, 87–93. - PubMed
-
- Jaipuri FA, Pohl NL, Org. Biomol. Chem 2008, 6, 2686–2691; - PubMed
- Tang S-L, Linz LB, Bonning BC, Pohl NLB, J. Org. Chem 2015, 80, 10482–10489; - PMC - PubMed
- Tang S-L, Pohl NLB, Org. Lett 2015, 17, 2642–2645; - PMC - PubMed
- Nagy G, Peng T, Kabotso DEK, Novotny MV, Pohl NLB, Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 13253–13256; - PMC - PubMed
- Tang S-L, Pohl NLB, Carbohydr. Res 2016, 430, 8–15. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

