Enhancer selection dictates gene expression responses in remote organs during tissue regeneration
- PMID: 35513710
- PMCID: PMC9107506
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-022-00906-y
Enhancer selection dictates gene expression responses in remote organs during tissue regeneration
Abstract
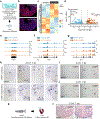
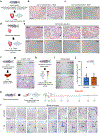
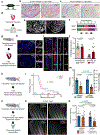
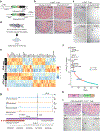
Acute trauma stimulates local repair mechanisms but can also impact structures distant from the injury, for example through the activity of circulating factors. To study the responses of remote tissues during tissue regeneration, we profiled transcriptomes of zebrafish brains after experimental cardiac damage. We found that the transcription factor gene cebpd was upregulated remotely in brain ependymal cells as well as kidney tubular cells, in addition to its local induction in epicardial cells. cebpd mutations altered both local and distant cardiac injury responses, altering the cycling of epicardial cells as well as exchange between distant fluid compartments. Genome-wide profiling and transgenesis identified a hormone-responsive enhancer near cebpd that exists in a permissive state, enabling rapid gene expression in heart, brain and kidney after cardiac injury. Deletion of this sequence selectively abolished cebpd induction in remote tissues and disrupted fluid regulation after injury, without affecting its local cardiac expression response. Our findings suggest a model to broaden gene function during regeneration in which enhancer regulatory elements define short- and long-range expression responses to injury.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of enhancer regulatory elements that direct epicardial gene expression during zebrafish heart regeneration.Development. 2022 Feb 15;149(4):dev200133. doi: 10.1242/dev.200133. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Development. 2022. PMID: 35179181 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of tissue repair by regeneration enhancer elements.Nature. 2016 Apr 14;532(7598):201-6. doi: 10.1038/nature17644. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27049946 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving Heart Regeneration by Replacement Histone Profiling.Dev Cell. 2017 Feb 27;40(4):392-404.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.01.013. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28245924 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of regulatory network predicts transcription factors driving the dynamics of zebrafish heart regeneration.Gene. 2022 Apr 20;819:146242. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146242. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35114280
-
Defining the acute kidney injury and repair transcriptome.Semin Nephrol. 2014 Jul;34(4):404-17. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Semin Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 25217269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Basic biology and roles of CEBPD in cardiovascular disease.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 14;11(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02357-4. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40087290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK signaling waves via body-wall muscles guide planarian whole-body regeneration across long distances.Cell Regen. 2023 Nov 8;12(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13619-023-00180-9. Cell Regen. 2023. PMID: 37938438 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration in adult Xenopus tropicalis evidenced by a transgenic reporter line.NPJ Regen Med. 2024 Dec 19;9(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41536-024-00384-w. NPJ Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 39702515 Free PMC article.
-
Foxm1 regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation in adult zebrafish after cardiac injury.Development. 2023 Mar 15;150(6):dev201163. doi: 10.1242/dev.201163. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Development. 2023. PMID: 36846912 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord repair is modulated by the neurogenic factor Hb-egf under direction of a regeneration-associated enhancer.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 11;14(1):4857. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40486-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37567873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poss KD, Wilson LG & Keating MT Heart regeneration in zebrafish. Science 298, 2188–2190 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

