Mechanics and functional consequences of nuclear deformations
- PMID: 35513718
- PMCID: PMC9902167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-022-00480-z
Mechanics and functional consequences of nuclear deformations
Abstract
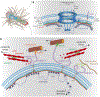
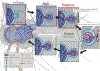
As the home of cellular genetic information, the nucleus has a critical role in determining cell fate and function in response to various signals and stimuli. In addition to biochemical inputs, the nucleus is constantly exposed to intrinsic and extrinsic mechanical forces that trigger dynamic changes in nuclear structure and morphology. Emerging data suggest that the physical deformation of the nucleus modulates many cellular and nuclear functions. These functions have long been considered to be downstream of cytoplasmic signalling pathways and dictated by gene expression. In this Review, we discuss an emerging perspective on the mechanoregulation of the nucleus that considers the physical connections from chromatin to nuclear lamina and cytoskeletal filaments as a single mechanical unit. We describe key mechanisms of nuclear deformations in time and space and provide a critical review of the structural and functional adaptive responses of the nucleus to deformations. We then consider the contribution of nuclear deformations to the regulation of important cellular functions, including muscle contraction, cell migration and human disease pathogenesis. Collectively, these emerging insights shed new light on the dynamics of nuclear deformations and their roles in cellular mechanobiology.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
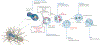

Similar articles
-
[Advances in cell nuclear mechanobiology and its regulation mechanisms].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Aug 25;40(4):617-624. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202304036. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37666750 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
The integration of tissue structure and nuclear function.Biochem Cell Biol. 2001;79(3):267-74. Biochem Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11467740 Review.
-
Nuclear Mechanotransduction in Skeletal Muscle.Cells. 2021 Feb 4;10(2):318. doi: 10.3390/cells10020318. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33557157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanical stability of the cell nucleus - roles played by the cytoskeleton in nuclear deformation and strain recovery.J Cell Sci. 2018 Jul 4;131(13):jcs209627. doi: 10.1242/jcs.209627. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29777038
-
Regulation of Nuclear Mechanics and the Impact on DNA Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 20;22(6):3178. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063178. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rethinking nuclear shaping: insights from the nuclear drop model.Soft Matter. 2024 Oct 2;20(38):7558-7565. doi: 10.1039/d4sm00683f. Soft Matter. 2024. PMID: 39105242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Tissue-Like, not Supraphysiological, Electrical Conductivity Stimulates Neuronal Lineage Specification through Calcium Signaling and Epigenetic Modification.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(35):e2400586. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400586. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38984490 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Biophysical Factors in Organ Development: Insights from Current Organoid Models.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;11(6):619. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11060619. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curved Nanofiber Network Induces Cellular Bridge Formation to Promote Stem Cell Mechanotransduction.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jan;10(3):e2204479. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204479. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36382560 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear shape is affected differentially by loss of lamin A, lamin C, or both lamin A and C.MicroPubl Biol. 2024 Feb 16;2024:10.17912/micropub.biology.001103. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001103. eCollection 2024. MicroPubl Biol. 2024. PMID: 38440331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Long JT & Lammerding J Nuclear Deformation Lets Cells Gauge Their Physical Confinement. Dev. Cell 56, 156–158 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

