Cost Analysis of Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Treatment Versus No Whole-Brain Radiotherapy After Stereotactic Radiosurgery and/or Surgery Among Adults with One to Three Melanoma Brain Metastases: Results from a Randomized Trial
- PMID: 35513735
- PMCID: PMC9283614
- DOI: 10.1007/s41669-022-00332-8
Cost Analysis of Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Treatment Versus No Whole-Brain Radiotherapy After Stereotactic Radiosurgery and/or Surgery Among Adults with One to Three Melanoma Brain Metastases: Results from a Randomized Trial
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to compare Australian health system costs at 12 months for adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) treatment after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and/or surgery versus observation among adults with one to three melanoma brain metastases. We hypothesized that treatment with adjuvant WBRT and subsequent healthcare would be more expensive than SRS/surgery alone.
Methods: The analysis was conducted alongside a multicentre, randomized phase III trial. A bespoke cost questionnaire was used to measure healthcare use, including hospitalizations, specialist and primary care visits, imaging, and medicines over 12 months. Mean per-patient costs were calculated based on the quantity of resources used and unit costs, reported in Australian dollars ($AU), year 2018 values. Skewness of cost data was determined using normality tests and censor-adjusted costs reported using the Kaplan-Meier sample average method. The analysis of difference in mean costs at each 2-month time point and at 12 months was performed and checked using Kruskal-Wallis, generalized linear models with gamma distribution and log link, modified Park test, ordinary least squares, and non-parametric bootstrapping.
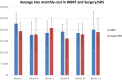
Results: In total, 89 patients with similar characteristics at baseline were included in the cost analysis (n = 43 WBRT; n = 46 observation). Hospitalization cost was the main cost, ranging from 63 to 89% of total healthcare costs. The unadjusted 12-monthly cost for WBRT was $AU71,138 ± standard deviation 41,475 and for observation $AU69,848 ± 33,233; p = 0.7426. The censor-adjusted 12-monthly cost for WBRT was $AU90,277 ± 36,274 and $AU82,080 ± 34,411 for observation. There was no significant difference in 2-monthly costs between groups (p > 0.30 for all models).
Conclusions: Most costs were related to inpatient hospitalizations associated with disease recurrence. Adding WBRT after local SRS/surgery for patients with one to three melanoma brain metastases did not significantly increase health system costs during the first 12 months.
Trial registration: ACTRN12607000512426, prospectively registered 14 September 2007.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Angela M Hong has received consultancy fees and honorarium from Amgen and Bayer. Anh D Tran, Mai TH Nguyen, Gerald Fogarty, Victoria Steel, Elizabeth Paton, and Rachael L Morton have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources