Clinical uses of Bupropion in patients with Parkinson's disease and comorbid depressive or neuropsychiatric symptoms: a scoping review
- PMID: 35513785
- PMCID: PMC9069850
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-022-02668-4
Clinical uses of Bupropion in patients with Parkinson's disease and comorbid depressive or neuropsychiatric symptoms: a scoping review
Abstract
Objective: Bupropion, an antidepressant inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and noradrenaline, should be useful to treat depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). Limited and conflicting literature data questioned its effectiveness and safety in depressed PD patients and extended its use to other neuropsychiatric symptoms associated with this disorder.
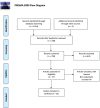
Design: The databases PubMed, Embase, Web of Sciences, Cochrane Library, and the grey literature were searched. Following a scoping review methodology, articles focusing on Bupropion uses in PD patients who manifested depressive or other neuropsychiatric alterations were reviewed.
Results: Twenty-three articles were selected, including 7 original articles, 3 systematic reviews or meta-analyses, 11 case reports, 1 clinical guideline, and 1 expert opinion. Bupropion showed considerable effectiveness in reducing depressive symptoms, particularly in relation to apathy. Solitary findings showed a restorative effect on compulsive behaviour secondary to treatment with dopamine as well as on anxiety symptoms. The effect on motor symptoms remains controversial. The safety profile of this medication seems positive, but additional precautions should be used in subjects with psychotic symptoms.
Conclusion: The available literature lacks good evidence to support the use of Bupropion in PD patients presenting depressive symptoms. Further investigations are needed to extend and confirm reported findings and to produce accurate clinical guidelines.
Keywords: Bupropion; Depression; Neuropsychiatric symptoms; Parkinson’s disease; Pharmacological treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Vismara is the Principal Investigator of the study “Bupropion for depression in Parkinson’s disease: clinical and epigenetic correlates” sponsored by “Aldo Ravelli” Center for Neurotechnology and Brain Therapeutic, University of Milan, Milan.
Prof. Dell’Osso has received Grant/Research Support from LivaNova, Inc., Angelini and Lundbeck and Lecture Honoraria from Angelini, FB Health and Lundbeck.
Prof. Priori, Dr. Nicolini, Dr. Benatti, Dr. Cova, Dr. Di Fonzo, Dr. Monfrini, Dr. Fetoni, and Dr. Viganò report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bupropion as the treatment of choice in depression associated with Parkinson's disease and it's various treatments.Med Hypotheses. 2010 Dec;75(6):544-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2010.07.024. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Med Hypotheses. 2010. PMID: 20708340
-
[Successful treatment of depression in a Parkinson disease patient with bupropion].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000 Nov 4;144(45):2157-9. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000. PMID: 11086491 Dutch.
-
Bupropion for the Treatment of Apathy in Alzheimer Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 May 1;3(5):e206027. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.6027. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32463470 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Review Update: Treatments for the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2011 Oct;26 Suppl 3(0 3):S42-80. doi: 10.1002/mds.23884. Mov Disord. 2011. PMID: 22021174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What can rodent models tell us about apathy and associated neuropsychiatric symptoms in Parkinson's disease?Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Mar 8;6(3):e753. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.17. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26954980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The use of sertraline to treat an adolescent of dystonia comorbid with major depressive disorder with psychotic features.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024 Mar;44(1):275-279. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12401. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 37987035 Free PMC article.
-
Slc4a7 Regulates Retina Development in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 5;25(17):9613. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179613. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273559 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the link between impulse control disorder and antidepressant use in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023 Dec;117:105918. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105918. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37922636 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Serotonylation and SERT Posttranslational Modifications in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Aging Dis. 2024 Mar 28;16(2):841-858. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0328. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39254383 Free PMC article. Review.