EIF4A3-regulated circ_0087429 can reverse EMT and inhibit the progression of cervical cancer via miR-5003-3p-dependent upregulation of OGN expression
- PMID: 35513835
- PMCID: PMC9069757
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02368-4
EIF4A3-regulated circ_0087429 can reverse EMT and inhibit the progression of cervical cancer via miR-5003-3p-dependent upregulation of OGN expression
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are noncoding RNAs with stable structures with high expression and tissue-specific expression. Studies have shown that circRNA dysregulation is closely related to the progression of tumours. However, the function and regulatory mechanism of most circRNAs in cervical cancer are still unclear. METHODS: CircRNAs related to cervical cancer were screened through the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. qRT-PCR was used to verify the expression of circ_0087429 in cervical cancer tissues and cells. Then, in vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted to evaluate the role of circ_0087429 in the progression of cervical cancer. The role of the circ_0087429/miR-5003-3p/osteoglycin (OGN) axis in the epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) was confirmed by rescue experiments, fluorescence in situ hybridization, luciferase reporter assays, immunofluorescence staining and western blotting. The inhibitory effect of Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III (EIF4A3) on the biogenesis of circ_0087429 was verified by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays and qRT-PCR.
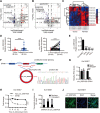
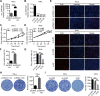
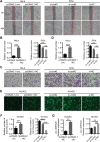
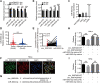
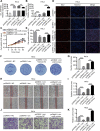
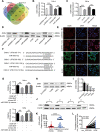
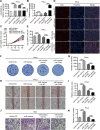
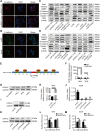
Results: circ_0087429 is significantly downregulated in cervical cancer tissues and cells and negatively correlated with International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) staging and lymphatic metastasis in cervical cancer patients. circ_0087429 can significantly inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of cervical cancer in vitro and tumour growth and metastasis in vivo. OGN is significantly downregulated in cervical cancer tissues and cells. circ_0087429 can upregulate the expression of OGN by competitively binding with miR-5003-3p, thereby reversing EMT and inhibiting the progression of cervical cancer. EIF4A3 can inhibit circ_0087429 expression by binding to its flanking regions.
Conclusions: As a tumour suppressor, circ_0087429 regulated by EIF4A3 can reverse EMT and inhibit the progression of cervical cancer through the miR-5003-3p/OGN axis. It is expected to become a potential target for the treatment of cervical cancer.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Circ_0087429; EIF4A3; Epithelial to mesenchymal transition; MiR-5003-3p; OGN.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EIF4A3-Induced Circ_0059914 Promoted Angiogenesis and EMT of Glioma via the miR-1249/VEGFA Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):973-987. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04319-w. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38951469
-
hsa_circ_0101119 facilitates the progression of cervical cancer via an interaction with EIF4A3 to inhibit TCEAL6 expression.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):654. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12293. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34278492 Free PMC article.
-
EIF4A3-induced circ_0084615 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer via miR-599/ONECUT2 pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jul 12;40(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02029-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34253241 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0067934 as a novel therapeutic target in cancer: From mechanistic to clinical perspectives.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154469. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154469. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37100022 Review.
-
MiR-1236: Key controller of tumor development and progression: Focus on the biological functions and molecular mechanisms.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154671. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154671. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37418995 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles and Potential Applications of Non-Coding RNAs in Cervical Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;13(7):1254. doi: 10.3390/genes13071254. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35886037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EIF4A3-mediated circ_0042881 activates the RAS pathway via miR-217/SOS1 axis to facilitate breast cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 25;14(8):559. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06085-4. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37626035 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoglycin: An ECM Factor Regulating Fibrosis and Tumorigenesis.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 11;12(11):1674. doi: 10.3390/biom12111674. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circIFNGR2 regulating ankylosing spondylitis-associated inflammation through macrophage polarization.iScience. 2023 Jul 10;26(8):107325. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107325. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37520722 Free PMC article.
-
The crosstalk between alternative splicing and circular RNA in cancer: pathogenic insights and therapeutic implications.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 16;29(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00662-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39550559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kalliala I, Athanasiou A, Veroniki AA, Salanti G, Efthimiou O, Raftis N, Bowden S, Paraskevaidi M, Aro K, Arbyn M, et al. Incidence and mortality from cervical cancer and other malignancies after treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Ann Oncol. 2020;31(2):213–227. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Simms KT, Hanley SJB, Smith MA, Keane A, Canfell K. Impact of HPV vaccine hesitancy on cervical cancer in Japan: a modelling study. The Lancet Public health. 2020;5(4):e223–e234. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675–691. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

