Interleukin-6 mediated inflammasome activation promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via JAK2/STAT3/Sox4/NLRP3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 35513871
- PMCID: PMC9069786
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02376-4
Interleukin-6 mediated inflammasome activation promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via JAK2/STAT3/Sox4/NLRP3 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been reported to be critical in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). However, the set of pathways that IL-6 might activate in OSCC are not fully understood.
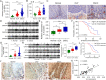
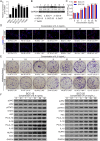
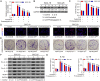
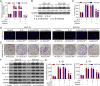
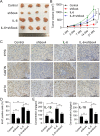
Methods: IL-6 and Sox4 expressions were first determined with RT-qPCR, ELISA, Western blot, or immunohistochemistry in OSCC tissues, and correlations between IL-6 and Sox4 expression and patient pathological characteristics were examined, and Kaplan-Meier approach was employed for evaluating the prognostic utility in OSCC patients. CCK-8, EdU stain and colony formation assays were utilized to test cell proliferation in vitro. Mechanistically, downstream regulatory proteins of IL-6 were verified through chromatin immunoprecipitation, luciferase reporter, pull-down, and the rescued experiments. Western blot was used for detecting protein expression. A nude mouse tumorigenicity assay was used to confirm the role of IL-6 and Sox4 in vivo.
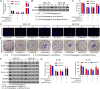
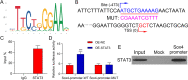
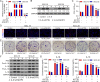
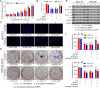
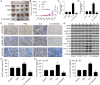
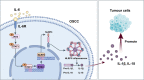
Results: IL-6 was upregulated in OSCC tissues, and Sox4 expression was positively correlated with IL-6 expression. High IL-6 and Sox4 expression was closely related to tumor size, TNM stage, and a poorer overall survival. Besides, IL-6 could accelerate OSCC cell proliferation by activating inflammasome via JAK2/STAT3/Sox4/NLRP3 pathways in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, STAT3 played as a transcription factor which positively regulated Sox4, and IL-6 promotes Sox4 expression by activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Moreover, through the rescue experiments, we further confirmed that IL-6 could promote proliferation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation via JAK2/STAT3/Sox4 pathway in OSCC cells. Finally, knockdown of Sox4 suppressed OSCC growth in vivo, and antagonized the acceleration of IL-6 on tumor growth.
Conclusions: We confirmed that IL-6 plays an oncogenic role in OSCC progression by activating JAK2/STAT3/Sox4/NLRP3 pathway, which might be the therapeutic targets for OSCC remedy.
Keywords: IL-6; JAK2; NLRP3 inflammasome; NLRP3 pathway; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; STAT3; Sox4.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang Y, Hu H, Wang Q, Li Z, Zhu Y, Zhang W, et al. The level and clinical significance of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study in 95 patients. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213(8):969–974. - PubMed
-
- Panarese I, Aquino G, Ronchi A, Longo F, Montella M, Cozzolino I, et al. Oral and Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic and predictive parameters in the etiopathogenetic route. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2019;19(2):105–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

