Network Analysis of Depressive Symptomatology in Underweight and Obese Adults
- PMID: 35514113
- PMCID: PMC9083035
- DOI: 10.1177/21501319221096917
Network Analysis of Depressive Symptomatology in Underweight and Obese Adults
Abstract
Background: Depressive symptoms can affect people's quality of life and social environment. In addition, in severe situations, they can lead to suicidal behaviors.
Objective: This study aimed to analyze the differences in depressive symptoms in underweight and obese Peruvian adults.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out based on secondary data obtained from the Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática (INEI), Lima, Peru. A sample of 10 053 participants was considered, of which 55.96% were women. Two Gaussian plot models were estimated and the levels of depressive symptomatology were compared between the 2 groups (adults with underweight and obese).
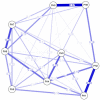
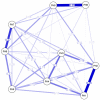
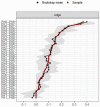
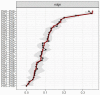
Results: A total of 1510 (15.02%) were underweight adults and 8543 (84.98%) were obese adults. There were differences in the reporting of depressive symptoms in the underweight group; the most central items were "Depressed mood" (PH2), "Tiredness/low energy" (PH4), and "Psychomotor difficulties" (PH8).
Conclusion: This study provides new evidence on the dynamic relationship between depressive symptoms according to the body mass index categories (underweight and obese) assessed.
Keywords: Peru; body mass index; depression; obesity; underweight.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
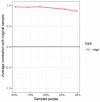
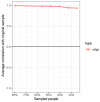
References
-
- Banda-Ccana DE, Infantes-Ruiz VH, Calizaya-Milla YE, et al.. Diet and risk of mental illness in Peruvian adults, cross-sectional study. Arch Latinoam Nutr. 2021;71:199-207.
-
- World Health Organization. Depression. 2020. Accessed February 20, 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
-
- Organización Panamericana de Salud. La carga de los trastornos mentales en la Región de las Américas, 2018. Organización Mundial de la Salud Oficina Regional para las Américas 2018;1-50.
-
- Instituto Nacional de Salud Mental. Estudio Epidemiológico de Salud Mental en Lima Metropolitana y Callao Replicación 2012. 2013;858:1-7.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

