Phosphorus containing analogues of SAHA as inhibitors of HDACs
- PMID: 35514164
- PMCID: PMC9090410
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2063281
Phosphorus containing analogues of SAHA as inhibitors of HDACs
Abstract
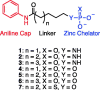
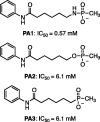
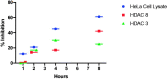
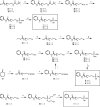
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are a family of enzymes responsible for regulating DNA transcription by modulating its binding to histone proteins. HDACs are overexpressed in several types of cancers and are recognised as drug targets. Vorinostat, or suberanilohydroxamic acid (SAHA), is an histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor with a hydroxamic acid as a zinc-binding group (ZBG), and it has been FDA approved for the treatment of T-cell lymphoma. In this work, phosphorus-based SAHA analogues were synthesised to assess their zinc-binding effectiveness compared to the hydroxamic acid of SAHA. Specifically, we examined phosphate, phosphoramidate and phosphorothiolate groups as isosteres of the canonical hydroxamic acid motif of conventional HDAC inhibitors. The compounds were screened for binding to HDAC enzymes from HeLa cell lysate. The most potent derivatives were then screened against HDAC3 and HDAC8 isoforms. HDAC inhibition assays demonstrated that these phosphorus-based SAHA analogs exhibited slow binding to HDACs but with greater potency than phosphonate SAHA analogs examined previously. All compounds inhibited HDACs, the most potent having an IC50 of 50 µM.
Keywords: HDAC; SAHA; phosphate; phosphoramidate; phosphorothiolate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial or personal interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structural requirements of histone deacetylase inhibitors: C4-modified SAHA analogs display dual HDAC6/HDAC8 selectivity.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:1790-1806. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.10.076. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29150330 Free PMC article.
-
The structural requirements of histone deacetylase inhibitors: SAHA analogs modified at the C5 position display dual HDAC6/8 selectivity.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Aug 1;27(15):3254-3258. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.06.033. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017. PMID: 28648461 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Requirements of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: SAHA Analogs Modified on the Hydroxamic Acid.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016 May;349(5):373-82. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201500472. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2016. PMID: 27062198 Free PMC article.
-
The Zinc-Binding Group Effect: Lessons from Non-Hydroxamic Acid Vorinostat Analogs.J Med Chem. 2023 Jun 22;66(12):7698-7729. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00226. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37276138 Review.
-
A promising future for breast cancer therapy with hydroxamic acid-based histone deacetylase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2025 Mar;156:108169. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108169. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Bioorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 39862739 Review.
Cited by
-
SAHA inhibits lung fibroblast activation by increasing p66Shc expression epigenetically.Aging Med (Milton). 2024 Dec 11;7(6):790-801. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12385. eCollection 2024 Dec. Aging Med (Milton). 2024. PMID: 39777101 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of triazolopyridine derivatives as potent JAK/HDAC dual inhibitors with broad-spectrum antiproliferative activity.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2409771. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2409771. Epub 2024 Oct 8. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39377432 Free PMC article.
-
Vorinostat attenuates UVB-induced skin senescence by modulating NF-κB and mTOR signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 29;15(1):10905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95624-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40158057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruce Alberts AJ, J, Lewis, M, Raff, et al. . Chromosomal DNA and its packaging in the chromatin fiber, In: Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science; 2002.
-
- Morales V, Giamarchi C, Chailleux C, et al. . Chromatin structure and dynamics: Functional implications. Biochimie 2001;83:1029–39. - PubMed
-
- Yang XJ, Seto E.. HATs and HDACs: from structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy and prevention. Oncogene 2007;26:5310–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
