12 Weeks of Physical Exercise Attenuates Oxidative Stress, Improves Functional Tests Performance, and Reduces Fall Risk in Elderly Women Independently on Serum 25(OH)D Concentration
- PMID: 35514345
- PMCID: PMC9065282
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.809363
12 Weeks of Physical Exercise Attenuates Oxidative Stress, Improves Functional Tests Performance, and Reduces Fall Risk in Elderly Women Independently on Serum 25(OH)D Concentration
Abstract
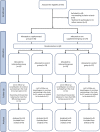
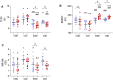
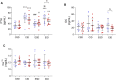
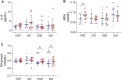
The study aimed to evaluate if the 25(OH)D concentration is related to physical training responses. Moreover, to determine the association between serum 25(OH)D concentration and older women's physical performance, oxidative stress markers, inflammation, and bone metabolism. 37 older women (age 72.9 ± 5.2 years) were assigned into two groups: supplemented (SG) and non-supplemented (NSG). Then, the participants from SG and NSG were randomly assigned into exercised and non-exercised groups: exercise sufficient vitamin D group (ESD; n = 10), exercise insufficient vitamin D group (EID; n = 9), control sufficient vitamin D group (CSD; n = 9), and control insufficient vitamin D group (CID; n = 9). To assess the study aims time up and go test (TUG), 6 min walk test (6MWT), fall risk test (FRT), blood osteocalcin (OC), parathormone (PTH), calcium (Ca2+), sulfhydryl groups (SH), malondialdehyde (MDA), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were performed. The results showed that a higher 25(OH)D concentration was in line with better physical performance and bone metabolism as well as lower inflammation. After 12 weeks of training we noted an improvement in 6MWT (from 374.0 ± 17.3 to 415.0 ± 18.8; p = 0.001 and from 364.8 ± 32.8 to 419.4 ± 32.3; p = 0.001 for EID and ESD, respectively), TUG (from 7.9 ± 0.5 to 6.8 ± 0.8; p = 0.001 and from 7.3 ± 1.5 to 6.4 ± 0.9; p = 0.002, for EID and ESD, respectively), reduction of fall risk (from 2.8 ± 0.8 to 1.9 ± 0.4; p = 0.003 and from 2.1 ± 1.1 to 1.6 ± 0.5; p = 0.047, for EID and ESD, respectively) and increase in SH groups (from 0.53 ± 0.06 to 0.58 ± 0.08; p = 0.012 and from 0.54 ± 0.03 to 0.59 ± 0.04; p = 0.005, for EID and ESD, respectively), regardless of the baseline 25(OH)D concentration. A decrease in PTH and OC concentration was observed only in EID group (from 57.7 ± 15.7 to 49.4 ± 12.6; p = 0.013 for PTH and from 27.9 ± 17.2 to 18.0 ± 6.2; p = 0.004 for OC). To conclude, vitamin D concentration among older women is associated with physical performance, fall risk, inflammation, and bone metabolism markers. Moreover, 12 weeks of training improved physical performance and antioxidant protection, regardless of baseline vitamin D concentration.
Keywords: aerobic training; bone metabolism; fall risk; healthy ageing; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 Rodziewicz-Flis, Kawa, Flis, Szaro-Truchan, Skrobot and Kaczor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation and influence of BsmI polymorphism of the VDR gene of the inflammatory profile and oxidative stress in elderly women with vitamin D insufficiency: Vitamin D3 megadose reduces inflammatory markers.Exp Gerontol. 2015 Jun;66:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2015.03.011. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Exp Gerontol. 2015. PMID: 25827670 Clinical Trial.
-
High prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in Morocco: relationship to lifestyle, physical performance, bone markers, and bone mineral density.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Jun;38(6):444-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.01.009. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 18336870
-
Effects of different doses of oral cholecalciferol on serum 25(OH)D, PTH, calcium and bone markers during fall and winter in schoolchildren.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010 Dec;64(12):1415-22. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2010.169. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20823895 Clinical Trial.
-
1alpha(OH)D3 One-alpha-hydroxy-cholecalciferol--an active vitamin D analog. Clinical studies on prophylaxis and treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in uremic patients on chronic dialysis.Dan Med Bull. 2008 Nov;55(4):186-210. Dan Med Bull. 2008. PMID: 19232159 Review.
-
Vitamin D physiology.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006 Sep;92(1):4-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.02.016. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16563471 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of exercise and antioxidant supplementation on cellular lipid peroxidation in elderly individuals: Systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 14;14:1113270. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1113270. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36866175 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia is associated with mortality in non-critical elderly patients visiting the emergency department.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 11;9:1027503. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1027503. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714126 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in selected exerkines concentration post folk-dance training are accompanied by glucose homeostasis and physical performance improvement in older adults.Sci Rep. 2023 May 26;13(1):8596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35583-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37237034 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Aspell N., Laird E., Healy M., Lawlor B., O'sullivan M. (2019). Vitamin D Deficiency is Associated with Impaired Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Clin. Interv. Aging 14, 1751–1761. 10.2147/cia.s222143 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachi A. L. L., Barros M. P., Vieira R. P., Rocha G. A., De Andrade P. B. M., Victorino A. B., et al. (2019). Combined Exercise Training Performed by Elderly Women Reduces Redox Indexes and Proinflammatory Cytokines Related to Atherogenesis. Oxid. Med. Cel Longev. 2019, 6469213. 10.1155/2019/6469213 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

