Improved therapeutic efficacy of quercetin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles on triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting uPA
- PMID: 35514369
- PMCID: PMC9056791
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra04231e
Improved therapeutic efficacy of quercetin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles on triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting uPA
Abstract
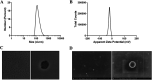
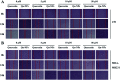
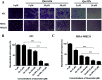
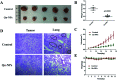
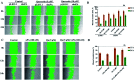
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is one kind of breast cancer that demonstrates highly aggressive tumor biology. The high heterogeneity of TNBC makes its individual clinical treatment extremely blind and limited, which also introduces more challenges into the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is a high level marker for breast cancer, which mediates tumor growth and metastasis. Quercetin is a plant-derived flavonoid in many plants, which inhibits uPA and has low bioavailability and mediocre pharmaceutical efficacy. Thus, we herein developed polymeric nanoparticulate systems from PLGA-TPGS (Qu-NPs) for quercetin oral delivery and evaluated the anticancer effect of this formulation on TNBC in vitro and in vivo. Qu-NPs have a uniform spherical morphology with a mean diameter of 198.4 ± 7.8 nm and good drug loading capacity (8.1 ± 0.4%). Moreover, Qu-NPs exhibited significantly improved inhibition on the growth and metastasis in TNBC cells. Following oral gavage, a remarkable antitumor effect of Qu-NPs on 4T1-bearing mice was observed with a tumor inhibition ratio of 67.88% and fewer lung metastatic colonies. Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of quercetin on the migration of uPA knockdown MDA-MB231 cells was greatly attenuated. Together, Qu-NPs improved the significant antitumor and antimetastatic effects by inhibiting uPA, which provides a new strategy for the treatment of TNBC.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
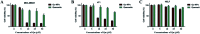
Similar articles
-
Nafamostat Mesylate in Combination with the Mouse Amino-Terminal Fragment of Urokinase-Human Serum Albumin Improves the Treatment Outcome of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy.Mol Pharm. 2023 Feb 6;20(2):905-917. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00297. Epub 2022 Dec 4. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36463525
-
Quercetin Has Antimetastatic Effects on Gastric Cancer Cells via the Interruption of uPA/uPAR Function by Modulating NF-κb, PKC-δ, ERK1/2, and AMPKα.Integr Cancer Ther. 2018 Jun;17(2):511-523. doi: 10.1177/1534735417696702. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Integr Cancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 28627240 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of growth and lung metastasis of breast cancer by tumor-homing triple-bioresponsive nanotherapeutics.J Control Release. 2020 Dec 10;328:454-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.08.066. Epub 2020 Sep 3. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32890553
-
Application of Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Quercetin in Cancer Cells.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(9):1107-1141. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230301121611. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 36856173 Review.
-
Expanding Arsenal against Neurodegenerative Diseases Using Quercetin Based Nanoformulations: Breakthroughs and Bottlenecks.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(7):1558-1574. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220810105421. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 35950245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Nanoformulations for Quercetin Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 5;15(6):1656. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061656. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Strategies for Cancer Therapy: Polymer Nanoparticles Carrying Medicinally Important Phytochemicals and Their Cellular Targets.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 1;15(11):2566. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112566. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging phytochemical-based nanocarriers: redefining the perspectives of breast cancer therapy.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 26. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04003-3. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40137964 Review.
-
Nano-Phytomedicine: Harnessing Plant-Derived Phytochemicals in Nanocarriers for Targeted Human Health Applications.Molecules. 2025 Jul 29;30(15):3177. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153177. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic and Oxidative Stress Inhibitory Activities of Terpenoids and Flavonols from Senegalia nigrescens (Oliv.) P.J.H. Hurter.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Fall;20(4):329-338. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2021.115653.15463. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 35194450 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

