Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3 Inhibition Relieves Mechanical Allodynia and Suppresses NLRP3 Inflammasome and NF-κB in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 35514432
- PMCID: PMC9063406
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.861312
Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3 Inhibition Relieves Mechanical Allodynia and Suppresses NLRP3 Inflammasome and NF-κB in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
Background: Neuroinflammation is critical in developing and maintaining neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury (SCI). The receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) has been shown to promote inflammatory response by exerting its non-necroptotic functions. In this study, we explored the involvement of RIPK3 in neuropathic pain after SCI.
Methods: Thoracic (T10) SCI rat model was conducted, and the mechanical threshold in rats was measured. The expressions of RIPK3, nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3), caspase-1, and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were measured with western blotting analysis or quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Double immunofluorescence staining was used to explore the colabeled NLRP3 with NeuN, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (IBA1). In addition, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was applied to analyze the levels of proinflammatory factors interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), interleukin 18 (IL-18), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α).
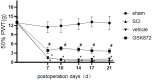
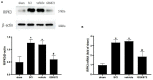
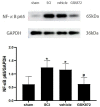
Results: The expression of RIPK3 was elevated from postoperative days 7-21, which was consistent with the development of mechanical allodynia. Intrathecal administration of RIPK3 inhibitor GSK872 could alleviate the mechanical allodynia in SCI rats and reduce the expression levels of RIPK3. The activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB was attenuated by GSK872 treatment. Furthermore, immunofluorescence suggested that NLRP3 had colocalization with glial cells and neurons in the L4-L6 spinal dorsal horns. In addition, GSK872 treatment reduced the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that RIPK3 was an important facilitated factor for SCI-induced mechanical allodynia. RIPK3 inhibition might relieve mechanical allodynia by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB, and the associated inflammation.
Keywords: GSK872; NLRP3 inflammasome; neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury; nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB); receptor-interacting protein kinase 3.
Copyright © 2022 Xue, Cao, Wang, Zhao, Han, Yang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

