Flaxseed orbitides, linusorbs, inhibit LPS-induced THP-1 macrophage inflammation
- PMID: 35514549
- PMCID: PMC9054600
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra09058d
Flaxseed orbitides, linusorbs, inhibit LPS-induced THP-1 macrophage inflammation
Abstract
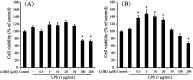
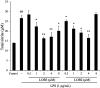
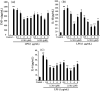
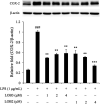
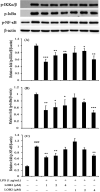
Linusorbs (flaxseed orbitides) are a family of naturally-occurring cyclic peptides. Previously, we reported that their anticancer effects were associated with their structures. In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory activities of 2 different linusorbs ([1-9-NαC]-linusorb B2 and [1-9-NαC]-linusorb B3) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced THP-1 macrophage activation as well as the underlying mechanism of this inflammatory response. Both molecules suppressed pro-inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, NO and COX-2) and were involved in downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. The suppressive effects on pro-inflammatory mediators were comparable and the concentration range of action was similar (1-4 μM). However, the concentration of compound that induced downregulation of the NF-κB pathway was different for each compound. While [1-9-NαC]-linusorb B3 could inhibit the activation of the NF-κB pathway at concentrations of 1 and 2 μM, [1-9-NαC]-linusorb B2 induced a comparable inhibitory effect at a concentration of 4 μM.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr Martin J. T. Reaney is the founder of, and has an equity interest in, PTD (Saskatoon, SK, Canada: previous company name is Prairie Tide Chemicals Inc.). Dr Youn Young Shim is a Market Consultant for PTD. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by the University of Saskatchewan (Saskatoon, SK, Canada) in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures
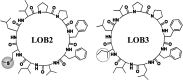
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

