Synthesis and characterization of a surface-grafted Pb(ii)-imprinted polymer based on activated carbon for selective separation and pre-concentration of Pb(ii) ions from environmental water samples
- PMID: 35514620
- PMCID: PMC9060653
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09992h
Synthesis and characterization of a surface-grafted Pb(ii)-imprinted polymer based on activated carbon for selective separation and pre-concentration of Pb(ii) ions from environmental water samples
Abstract
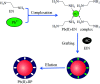
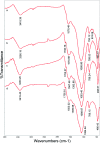
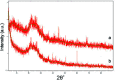
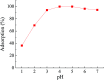
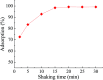
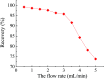
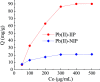
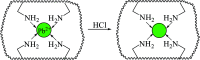
Even the lowest concentration level of lead (Pb) in the human body is dangerous to health due to its bioaccumulation and high toxicity. Therefore, it is very important to develop selective and fast adsorption methods for the removal of Pb(ii) from various samples. In this paper, a new Pb(ii) ion-imprinted polymer (Pb(ii)-IIP) was prepared with surface imprinting technology by using lead nitrate as a template, for the solid-phase extraction of trace Pb(ii) ions in environmental water samples. The imprinted polymer was characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms. The separation/pre-concentration conditions for Pb(ii) were investigated, including the effects of pH, shaking time, sample flow rate, elution conditions and interfering ions. Compared with non-imprinted particles, the ion-imprinted polymer had a higher selectivity and adsorption capacity for Pb(ii). The pseudo-second-order kinetics model and Langmuir isotherm model fitted well with the adsorption data. The relative selectivity factor values (α r) of Pb(ii)/Zn(ii), Pb(ii)/Ni(ii), Pb(ii)/Co(ii) and Pb(ii)/Cu(ii) were 168.20, 192.71, 126.13 and 229.39, respectively, which were all much greater than 1. The prepared Pb(ii)-imprinted polymer was shown to be promising for the separation/pre-concentration of trace Pb(ii) from natural water samples. The adsorption and desorption mechanisms were also proposed.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption performance of Pb(II)-imprinted polymer in nano-TiO2 matrix.J Environ Sci (China). 2009;21(12):1722-9. doi: 10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62479-1. J Environ Sci (China). 2009. PMID: 20131604
-
Novel magnetic ion-imprinted polymer: an efficient polymeric nanocomposite for selective separation and determination of Pb ions in aqueous media.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Sep;25(26):26297-26306. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2680-0. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29978316
-
Selective adsorption behavior of Pb(II) by mesoporous silica SBA-15-supported Pb(II)-imprinted polymer based on surface molecularly imprinting technique.J Hazard Mater. 2011 Feb 15;186(1):197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.105. Epub 2010 Nov 4. J Hazard Mater. 2011. PMID: 21109351
-
Facile preparation of a nano-imprinted polymer on magnetite nanoparticles for the rapid separation of lead ions from aqueous solution.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018 May 9;20(18):12870-12878. doi: 10.1039/c8cp01163j. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018. PMID: 29700530
-
Application Prospect of Ion-Imprinted Polymers in Harmless Treatment of Heavy Metal Wastewater.Molecules. 2024 Jul 2;29(13):3160. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133160. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999112 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selected pharmaceuticals removal using algae derived porous carbon: experimental, modeling and DFT theoretical insights.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 28;9(17):9792-9808. doi: 10.1039/c9ra01086f. eCollection 2019 Mar 22. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zargar B. Khazaeifar A. Microchim. Acta. 2017;184:4521–4529. doi: 10.1007/s00604-017-2489-4. - DOI
-
- Li N. Jiang H. L. Wang X. Wang X. Xu G. Zhang B. Wang L. Zhao R. S. Lin J. M. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2018;102:60–74. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.01.009. - DOI
-
- Poole C. F. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2003;22:362–373. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(03)00605-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

