ASK1-p38 cascaded signal mediates pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier injury induced by the return of PHSML in rats
- PMID: 35514647
- PMCID: PMC9060572
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra08473d
ASK1-p38 cascaded signal mediates pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier injury induced by the return of PHSML in rats
Abstract
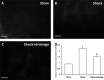
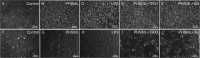
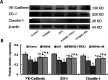
The return of post-hemorrhagic shock mesenteric lymph (PHSML) induces pulmonary vascular endothelial barrier dysfunction, which results in acute lung injury. Activation of the apoptosis signal-regulated kinase 1 (ASK1) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) pathway has been shown to trigger inflammatory responses. However, whether the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway is involved in the PHSML-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction remains unclear. In the present study, permeability changes of pulmonary capillaries were found in vivo, and activation of the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway was determined in vitro. PMVEC barrier dysfunction was determined by measuring TEER. Furthermore, junctional and cytoskeletal protein expressions were analyzed. The results showed that hemorrhagic shock led to a marked increase in the permeability of pulmonary capillaries in vivo, which was markedly alleviated by PHSML drainage. In cultured pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs), PHSML reduced the endothelial barrier function accompanied by upregulated p-ASK1 and p-p38 MAPK protein expression, impaired the cytoskeletal protein structure, and down-regulated junction protein expression. These adverse effects were eliminated by applying either Trx1 (ASK1 inhibitor) or SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor). These results indicated that the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway mediates PHSML-induced pulmonary vascular endothelial barrier dysfunction during hemorrhagic shock.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

