Retracted Article: Gemcitabine aggravates miR-199a-5p-mediated breast cancer cell apoptosis by promoting VEGFA downregulation via inactivating the AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 35514680
- PMCID: PMC9065560
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra00016j
Retracted Article: Gemcitabine aggravates miR-199a-5p-mediated breast cancer cell apoptosis by promoting VEGFA downregulation via inactivating the AKT signaling pathway
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Gemcitabine aggravates miR-199a-5p-mediated breast cancer cell apoptosis by promoting VEGFA downregulation via inactivating the AKT signaling pathway.RSC Adv. 2021 May 5;11(27):16478. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90114a. eCollection 2021 Apr 30. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35481960 Free PMC article.
Abstract
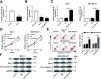
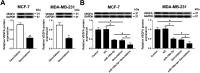
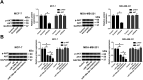
Breast cancer is the most frequent malignancy diagnosed in women, and Gemcitabine-based therapy is frequently used to treat late-stage breast cancer. miR-199a-5p plays a tumor-suppressive role in breast cancer. This work aimed to explore the mechanism of miR-199a-5p plus Gemcitabine in breast cancer cells. Expression of miR-199a-5p was measured by RT-qPCR, while expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) was measured by Western blot and RT-qPCR. Overexpression of miR-199a-5p and/or silencing of VEGFA was obtained using transfection in breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Functional experiments were performed to explore cell viability, apoptosis rate, and expressions of apoptosis-related genes: cell viability was assessed by MTT staining, apoptosis rate was recorded by flow cytometry, and Western blot was used to evaluate the expressions of Bcl-2, Bax and cleaved caspase 3. The signaling pathway was studied with respect to AKT activity via determination of p-AKT expression levels. Our study found that miR-199a-5p was downregulated and VEGFA was upregulated in breast cancer tissues and cells. Overexpression of miR-199a-5p and/or silencing of VEGFA contributed to cell apoptosis and inhibited cell viability, which was promoted by Gemcitabine. VEGFA was a downstream target of miR-199a-5p, and was negatively regulated by Gemcitabine. Moreover, Gemcitabine aggravated the miR-199a-5p-induced suppression of the VEGFA level and AKT activity in breast cancer cells. Our data show that Gemcitabine aggravates miR-199a-5p-mediated VEGFA downregulation and apoptosis via inactivating the AKT signaling pathway in breast cancer cells, indicating a novel promising combined therapy of miR-199a-5p overexpression and Gemcitabine.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retraction: Gemcitabine aggravates miR-199a-5p-mediated breast cancer cell apoptosis by promoting VEGFA downregulation via inactivating the AKT signaling pathway.RSC Adv. 2021 May 5;11(27):16478. doi: 10.1039/d1ra90114a. eCollection 2021 Apr 30. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35481960 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing long non-coding RNAs nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase antisense RNA 1 inhibited papillary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion and promoted apoptosis via targeting miR-199a-5p.Endocr J. 2021 May 28;68(5):583-597. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0353. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Endocr J. 2021. PMID: 33612561
-
miR-199a-5p confers tumor-suppressive role in triple-negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 14;16(1):887. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2916-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27842518 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulating NEAT1 inhibited the viability and vasculogenic mimicry formation of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma cells via miR-195-5p/VEGFA axis.Biosci Rep. 2020 Nov 27;40(11):BSR20201373. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201373. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33146672 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA H19 upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor A to enhance mesenchymal stem cells survival and angiogenic capacity by inhibiting miR-199a-5p.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Apr 19;9(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0861-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29673400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang L. Sun T. T. Wang N. Zhonghua Yufang Yixue Zazhi. 2012;46:1009–1014. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

