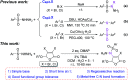
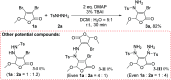
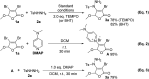
Quick construction of a C-N bond from arylsulfonyl hydrazides and Csp2-X compounds promoted by DMAP at room temperature
- PMID: 35514736
- PMCID: PMC9065325
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03403j
Quick construction of a C-N bond from arylsulfonyl hydrazides and Csp2-X compounds promoted by DMAP at room temperature
Abstract
An efficient approach for C-N bond construction by the coupling reaction of arylsulfonyl hydrazides and Csp2-X compounds is described for the first time with good yields at room temperature. The reaction promoted by the simple base DMAP displays excellent regioselectivity as well as high functional group tolerance with 41 examples. Even for inactive Csp2-Cl compounds, the metal-free transformation also affords a satisfactory yield after prolonging the reaction time, which is comparable to that of the corresponding Csp2-Br compound. The good effect of DMAP and its action mechanism are confirmed by the competitive experiments of reactivity between Cl-substituted and Br-substituted substrates and the single-crystal X-ray analysis of the key intermediate quaternary ammonium salt. Importantly, the application of this method for a gram-scale (even over 10 g) preparation can be accomplished.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Namba K. Takeuchi K. Kaihara Y. Oda M. Nakayama A. Nakayama A. Yoshida M. Tanino K. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:8731. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9731. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Huang Z.-X. Wang C.-P. Dong G.-B. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016;55:5299. doi: 10.1002/anie.201600912. - DOI - PubMed
- Sun Q. Li L.-G. Liu L.-Y. Guan Q.-Q. Yang Y. Zha Z.-G. Wang Z.-Y. Org. Lett. 2018;20:5592. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b02268. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li S.-Y. Li X. Yang F. Wu Y.-J. Org. Chem. Front. 2015;2:1076. doi: 10.1039/C5QO00212E. - DOI
- Zhao Y. Lai Y.-L. Du K.-S. Lin D.-Z. Huang J.-M. J. Org. Chem. 2017;82:9655. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b01741. - DOI - PubMed
- Peng Z.-H. Zheng X. Zhang Y.-J. An D.-L. Dong W.-R. Green Chem. 2018;20:1760. doi: 10.1039/C8GC00381E. - DOI
- Zhu X.-T. Lu Q.-L. Wang X. Zhang T.-S. Hao W.-J. Tu S.-J. Jiang B. J. Org. Chem. 2018;83:9890. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b01343. - DOI - PubMed
- Liu L.-X. Sun K. Su L.-B. Dong J.-Y. Cheng L. Zhu X. D. Au C. T. Zhou Y. B. Yin S. F. Org. Lett. 2018;20:4023. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01585. - DOI - PubMed
- Ni J.-B. Xue Y. Sun L.-P. Zhang A. J. Org. Chem. 2018;83:4598. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b00341. - DOI - PubMed
- Yao B. Miao T. Li P. Wang L. Org. Lett. 2019;21:124. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03564. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang G. Y. Lv S. S. Shoberu A. Zou J. P. J. Org. Chem. 2017;82:9801. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b01121. - DOI - PubMed
- Yu Q. Yang Y. Wan J.-P. Liu Y. J. Org. Chem. 2018;83:11385. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.8b01658. - DOI - PubMed
- Bao Y.-S. Yang X.-Q. Zhou Q.-F. Yang F. Org. Lett. 2018;20:1966. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00511. - DOI - PubMed
- Yang Z. Yan Y.-Q. Li A. Liao J.-S. Zhang L. Yang T. Zhou C.-S. New J. Chem. 2018;42:14738. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ03461C. - DOI
- Hou Y.-L. Zhu L.-Y. Hu H. Chen S.-W. Li Z.-F. Liu Y. J. Gong P. New J. Chem. 2018;42:8752. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ01145A. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources