Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: anticancer and antimicrobial activities
- PMID: 35514831
- PMCID: PMC9064228
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra01659g
Biogenesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Pandanus odorifer leaf extract: anticancer and antimicrobial activities
Abstract
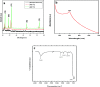
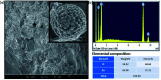
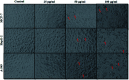
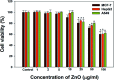
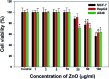
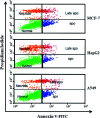
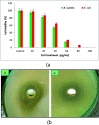
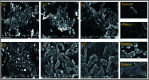
The continuously increasing incidence rates of cancer and infectious diseases are open threats to the sustainable survival of animals and humans. In the last two decades, the demands of nanomaterials as modern therapeutic agents have increased. In this study, biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were developed from aqueous Pandanus odorifer leaf extract (POLE) and characterized using modern methods and tools, such as electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and UV-vis spectroscopy, which indicated the formation of very pure, spherical NPs approximately 90 nm in size. The anticancer activity of the ZnO NPs was evaluated by MTT and neutral red uptake (NRU) assays in MCF-7, HepG2 and A-549 cells at different doses (1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 μg ml-1). Moreover, the morphology of the treated cancer cells was examined by phase contrast microscopy. The results suggest that the synthesized ZnO NPs inhibited the growth of the cells when applied a concentration from 50-100 μg ml-1. Moreover, the biogenic ZnO NPs were analysed as an antimicrobial agent against pathogenic bacteria. The highest antibacterial activity was observed against Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis (26 nm) and Gram-negative Escherichia coli (24 mm) at 50 μg per well. Complete bacterial growth (100%) vanished 100% upon treatment with ZnO NPs at 85 μg ml-1. Overall, POLE mediated derived biogenic ZnO NPs could serve as a significant anticancer and antimicrobial agent and be used in the development of novel drugs and skin care products.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mycogenic Synthesis of Extracellular Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Xylaria acuta and Its Nanoantibiotic Potential.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 2;15:8519-8536. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S271743. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33173290 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Pelargonium odoratissimum (L.) Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1444. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081444. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892646 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Dec 20;14:87-100. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S186888. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30587987 Free PMC article.
-
Biological therapeutics of Pongamia pinnata coated zinc oxide nanoparticles against clinically important pathogenic bacteria, fungi and MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Microb Pathog. 2017 Mar;104:268-277. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.01.029. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28115262
-
Biogenic fabrication of nanomaterials from flower-based chemical compounds, characterization and their various applications: A review.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020 Oct;27(10):2551-2562. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 11. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32994711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bio Framework-Derived Facile MoO3-NiO-PdO-Pd Nanomaterial for Detoxification of Organic Pollutants.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Aug 6;15:5591-5602. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S259550. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32848389 Free PMC article.
-
Organic template-assisted green synthesis of CoMoO4 nanomaterials for the investigation of energy storage properties.RSC Adv. 2020 Feb 25;10(14):8115-8129. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09477f. eCollection 2020 Feb 24. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497827 Free PMC article.
-
Croton macrostachyus Leaf Extract-Mediated Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and ZnO/CuO Nanocomposites for the Enhanced Photodegradation of Methylene Blue Dye with the COMSOL Simulation Model.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 19;9(1):559-572. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06155. eCollection 2024 Jan 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38222549 Free PMC article.
-
Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cocos nucifera leaf extract: characterization, antimicrobial, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity.R Soc Open Sci. 2022 Nov 23;9(11):220858. doi: 10.1098/rsos.220858. eCollection 2022 Nov. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 36425517 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of zinc oxide and silver/zinc oxide nanoparticles from Urginea epigea for antibacterial and antioxidant applications.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 10;8(12):e12243. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12243. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36593860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A Detail Investigation to Observe the Effect of Zinc Oxide |Nanoparticle| Zinc Oxide, 2019. Available from: https://www.scribd.com/document/89002172/A-Detail-Investigation-to-Obser...
-
- Sahoo S., Socio-ethical issues and nanotechnology development: Perspectives from India, 10th IEEE International Conference on Nanotechnology, IEEE, 2010. , pp. 1205–10. Available from: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5697887/
-
- Bhattacharyya D., Singh S., Satnalika N., Khandelwal A., Jeon S.-H., Nanotechnology, Big things from a Tiny World: a Review, International Journal of u-and e-Service, 2009, Vol. 2. Available from: https://www.ida.liu.se/∼TGTU51/articles/MPN-paper.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

