Transformation of novel TiOF2 nanoparticles to cluster TiO2-{001/101} and its degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride under simulated sunlight
- PMID: 35514916
- PMCID: PMC9058001
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra08476j
Transformation of novel TiOF2 nanoparticles to cluster TiO2-{001/101} and its degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride under simulated sunlight
Abstract
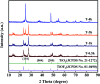
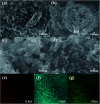
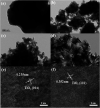
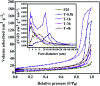
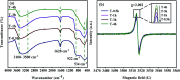
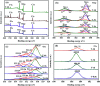
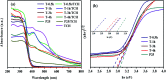
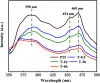
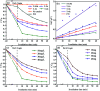
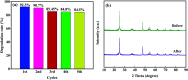
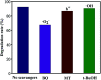
The anatase type cluster TiO2-{001/101} was rapidly generated by a one-step hydrothermal method. The transformation process of coral-like TiOF2 nanoparticles to cluster TiO2-{001/101} was investigated for the first time, and the sensitization between cluster TiO2-{001/101} and tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH) was also discussed. The degradation rate of TCH by cluster TiO2-{001/101} under simulated sunlight was 92.3%, and the total removal rate was 1.76 times that of P25. Besides, cluster TiO2-{001/101} settles more easily than P25 in deionized water. The study showed that cluster TiO2-{001/101} derived from coral-like TiOF2 nanoparticles had a strong adsorption effect on TCH, which was attributed to the oxygen vacancy (Ov) and {001} facets of cluster TiO2-{001/101}. The strong adsorption effect promoted the sensitization between cluster TiO2-{001/101} and TCH, and widened the visible light absorption range of cluster TiO2-{001/101}. In addition, the fluorescence emission spectrum showed that cluster TiO2-{001/101} had a lower luminous intensity, which was attributed to the heterojunction formed by {001} facets and {101} facets that reduces the recombination rate of carriers. It should be noted that cluster TiO2-{001/101} still has good degradation performance for TCH after five cycles of degradation. This study provides a new idea for the synthesis of cluster TiO2-{001/101} with high photocatalytic performance for the treatment of TCH wastewater.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests exiting in the manuscript submission, and it is approved by all of the authors for publication. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript to be enclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Lv C. Lan X. Wang L. Dai X. Zhang M. Cui J. Yuan S. Wang S. Shi J. Environ. Technol. 2019:11. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Q. Sun Y. Na F. Wei J. Xu S. Li Y. Guo F. Appl. Catal., B. 2019;254:541–550. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.05.006. - DOI
-
- Yang W. Han Y. Li C. Zhu L. Shi L. Tang W. Wang J. Yue T. Li Z. Chem. Eng. J. 2019;375:122076. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122076. - DOI
-
- Miao J. Wang F. Chen Y. Zhu Y. Zhou Y. Zhang S. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019;475:549–558. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.036. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

