miR-582 Suppresses the Proliferation of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (BCP-ALL) Cells and Protects Them From Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity
- PMID: 35514986
- PMCID: PMC9065596
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.853094
miR-582 Suppresses the Proliferation of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (BCP-ALL) Cells and Protects Them From Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity
Abstract
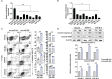
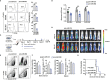
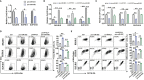
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL) is a malignancy characterized by the aberrant accumulation of immature B-cell precursors in bone marrow and other lymphoid organs. Although several intrinsic regulatory signals participating in BCP-ALL have been clarified, detailed intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms that regulate BCP-ALL progression have not been fully understood. In the current study, we report that miR-582 is downregulated in BCP-ALL cells compared with normal B cells. Forced overexpression of miR-582 attenuated BCP-ALL cell proliferation and survival. We found that miR-582 overexpression disturbed the mitochondrial metabolism of BCP-ALL cells, leading to less ATP but more ROS production. Mechanistically, we identified PPTC7 as a direct target of miR-582. MiR-582 overexpression inhibited the activity of CoQ10, which is downstream of PPTC7 and played an important positive regulatory role in mitochondrial electron transportation. Finally, we found that overexpression of miR-582 upregulated the expression of immune checkpoint molecule CD276 and reduced NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against BCP-ALL cells. CD276 blockade significantly increased NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against miR-582-overexpressing BCP-ALL cells. Together, our research demonstrates that miR-582 acts as a negative regulator of BCP-ALL cells by reducing proliferation and survival, but protects BCP-ALL cells from NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, suggesting that miR-582 may be a new therapeutic biomarker for BCP-ALL with CD276 blocker.
Keywords: BCP-ALL; CD276; NK cells; PPTC7; immune checkpoint; metabolism; miR-582; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhang, He, Gao, Che, Cao, Huang, Zheng and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A regulatory loop among CD276, miR-29c-3p, and Myc exists in cancer cells against natural killer cell cytotoxicity.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119438. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119438. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33798549
-
Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14359. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214359. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430839 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow T helper cells with a Th1 phenotype induce activation and proliferation of leukemic cells in precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients.Oncogene. 2019 Mar;38(13):2420-2431. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0594-4. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30532071
-
Contribution of the TIME in BCP-ALL: the basis for novel approaches therapeutics.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 17;14:1325255. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1325255. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38299154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Puppet masters of B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: The preB cell receptor and the interleukin 7 receptor α.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Apr;53(4):e2250093. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250093. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36805963 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of exhausted natural killer cells in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of leukemia.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 22;22(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01428-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38254135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the Regulatory Role of microRNAs in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241273143. doi: 10.1177/15330338241273143. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39099455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1737. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031737. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339019 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDC1 is a therapeutic target for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by attenuating DNA damage response through the KMT2C-H3K4me1/me3 epigenetic axis.Leukemia. 2025 Feb;39(2):308-322. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02451-z. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 39501105
-
Ribosomal protein L9 is a potential therapeutic target for B-ALL through the activation of the p53 signaling pathway.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 27;16:1560706. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560706. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40213545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heisterkamp N, ji Joo E, Yang L, Groffen J, Fei F. Cell-Intrinsic and Extrinsic Effects of Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. bioRxiv (2021). doi: 10.1101/2021.09.22.461145 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

