Interleukin-17 Links Inflammatory Cross-Talks Between Comorbid Psoriasis and Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35514987
- PMCID: PMC9063001
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835671
Interleukin-17 Links Inflammatory Cross-Talks Between Comorbid Psoriasis and Atherosclerosis
Abstract
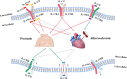
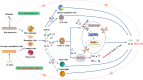
Psoriasis is a chronic, systemic, immune-mediated inflammatory disorder that is associated with a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Studies have shown that psoriasis often coexists with atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease of large and medium-sized arteries, which is a major cause of CVD. Although the molecular mechanisms underlying this comorbidity are not fully understood, clinical studies have shown that when interleukin (IL)-17A inhibitors effectively improve psoriatic lesions, atherosclerotic symptoms are also ameliorated in patients with both psoriasis and atherosclerosis. Also, IL-17A levels are highly expressed in the psoriatic lesions and atherosclerotic plaques. These clinical observations implicit that IL-17A could be a crucial link for psoriasis and atherosclerosis and IL-17A-induced inflammatory responses are the major contribution to the pathogenesis of comorbid psoriasis and atherosclerosis. In this review, the current literature related to epidemiology, genetic predisposition, and inflammatory mechanisms of comorbidity of psoriasis and atherosclerosis is summarized. We focus on the immunopathological effects of IL-17A in both diseases. The goal of this review is to provide the theoretical base for future preventing or treating psoriasis patients with atherosclerosis comorbidity. The current evidence support the notion that treatments targeting IL-17 seem to be hold some promise to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with psoriasis.
Keywords: IL-23 / IL-17 axis; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; interleukin (IL)-17; interleukin (IL)-17A; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Zang, Liu, Yan and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunoglobulin E, the potential accelerator of comorbid psoriasis and atherosclerosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Feb;183:117860. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.117860. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 39848109 Review.
-
IL-17 Pathway Members as Potential Biomarkers of Effective Systemic Treatment and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):555. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010555. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008981 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiling reveals interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody treatment ameliorate lipids metabolism with the potentiality to reduce cardiovascular risk in psoriasis patients.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Feb 18;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01441-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 33602246 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Treatment with IL-17/IL-23 Inhibitors on Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Plaque Psoriasis and/or Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 23;11(2):318. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020318. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-17A causes depression-like symptoms via NFκB and p38MAPK signaling pathways in mice: Implications for psoriasis associated depression.Cytokine. 2017 Sep;97:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 May 29. Cytokine. 2017. PMID: 28570931
Cited by
-
Inflammatory Immune Markers Associated With Thyroid Peroxidase Autoantibodies in Children Diagnosed With Both Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease.Scand J Immunol. 2025 Apr;101(4):e70015. doi: 10.1111/sji.70015. Scand J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40170218 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Involvement of New Members of the Interleukin Family in Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025;21(4):e1573403X330079. doi: 10.2174/011573403X330079241213071055. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39844544 Review.
-
Residual non-specific and disease-specific inflammatory markers in successfully treated young psoriasis patients: a cross-sectional study.Immunol Res. 2025 Jan 8;73(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09584-4. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 39775226 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis Beyond the Skin: A Disease With Cardiovascular Risk.Cureus. 2025 Jul 21;17(7):e88464. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88464. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40698258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Femoral Atherosclerotic Plaque in Psoriasis Patients and Controls: A Case-Control Study.J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2024 Sep 30:24755303241288541. doi: 10.1177/24755303241288541. Online ahead of print. J Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis. 2024. PMID: 39544332 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

