EDTA-bonded multi-connected carbon-dots and their Eu3+ complex: preparation and optical properties
- PMID: 35515301
- PMCID: PMC9062604
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra01521c
EDTA-bonded multi-connected carbon-dots and their Eu3+ complex: preparation and optical properties
Abstract
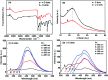
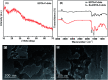
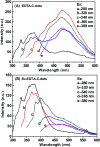
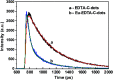
EDTA-bonded multi-connected carbon-dots (EDTA-C-dots) were prepared from carbon dot precursors and complexed with Eu3+ to give Eu3+-coordinated EDTA-bonded multi-connected carbon dots (Eu-EDTA-C-dots). Whereas EDTA-C-dots were readily soluble in DMSO, Eu-EDTA-C-dots could not be easily dissolved in DMSO, water, or other common organic solvents. The newly prepared materials were thoroughly characterized. The X-ray diffraction results showed that no crystalline phase of Eu oxides (europium oxide or europium hydroxide) could be observed in Eu-EDTA-C-dots. The infrared and UV-Vis spectra showed that coordination with Eu3+ ions did not damage the structure of the EDTA-C-dots. It was found that EDTA could be easily grafted on the surface of carbon dots and EDTA had minimal influence on the photoluminescence of the carbon dot matrix. In contrast, the existence of Eu3+ ions strongly quenched the photoluminescence of Eu-EDTA-C-dots. The measured and fitted decay lifetime indicated that Eu-EDTA-C-dots possessed two photoluminescence decay processes, i.e., radiative recombination and non-radiative recombination.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microwave-Assisted Polyol Synthesis of Water Dispersible Red-Emitting Eu3+-Modified Carbon Dots.Materials (Basel). 2016 Dec 29;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/ma10010025. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28772378 Free PMC article.
-
Structural effects on the photophysical properties of mono-β-diketonate and bis-β-diketonate Eu(III) complexes.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015 Jun 28;17(24):16136-44. doi: 10.1039/c5cp01392e. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2015. PMID: 26031613
-
Eu3+ amidst ionic copper in glass: Enhancement through energy transfer from Cu+, or quenching by Cu2+?Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017 Feb 15;173:979-985. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017. PMID: 27840046
-
Highly efficient luminescent hybrid materials covalently linking with europium(III) complexes via a novel fluorinated beta-diketonate ligand: synthesis, characterization and photophysical properties.Dalton Trans. 2010 Sep 14;39(34):8084-92. doi: 10.1039/c0dt00316f. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Dalton Trans. 2010. PMID: 20628688
-
Assessment of spectroscopic parameters of solvated Eu(dmh)3 phen organometallic complex in various basic and acidic solvents.Luminescence. 2018 Aug;33(5):968-980. doi: 10.1002/bio.3497. Epub 2018 May 31. Luminescence. 2018. PMID: 29851237
Cited by
-
PEI functionalized NaCeF4:Tb3+/Eu3+ for photoluminescence sensing of heavy metal ions and explosive aromatic nitro compounds.RSC Adv. 2021 May 27;11(32):19333-19350. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02910j. eCollection 2021 May 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479215 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrothermally activated TiO2 nanoparticles with a C-dot/g-C3N4 heterostructure for photocatalytic enhancement.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 May 25;3(14):4089-4097. doi: 10.1039/d1na00213a. eCollection 2021 Jul 13. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36132837 Free PMC article.
-
Electron/energy co-transfer behavior and reducibility of Cu-chlorophyllin-bonded carbon-dots.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 26;10(52):31495-31501. doi: 10.1039/d0ra04958a. eCollection 2020 Aug 21. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520672 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

